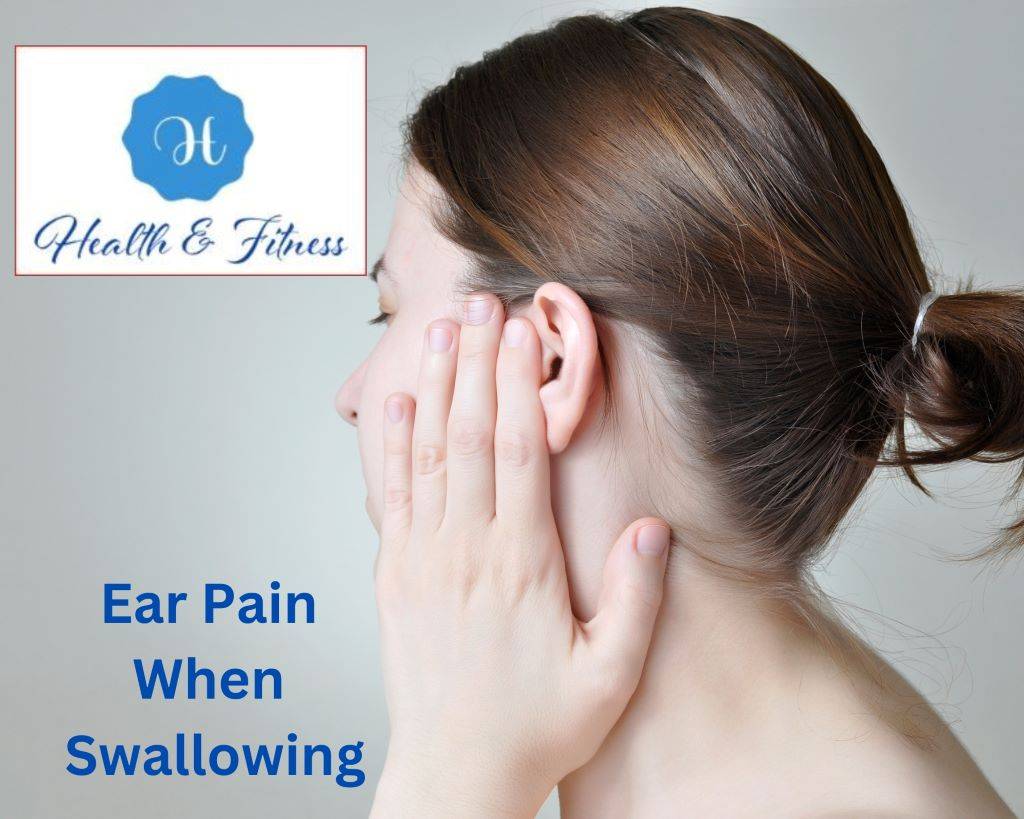
Do you often experience a sharp twinge or discomfort in your ear whenever you swallow? If so, you’re not alone. Ear pain when swallowing, medically known as “odynophagia,” is a common yet often overlooked symptom that can indicate an underlying health issue. This comprehensive guide will explore the various causes, symptoms, and potential solutions to this problem.
Understanding Ear Pain When Swallowing
What is Ear Pain When Swallowing?
Ear pain when swallowing refers to discomfort, tenderness, or sharp pain in one or both ears. It can range from a mild annoyance to intense throbbing, making even simple tasks like eating, drinking, or talking an uncomfortable ordeal. Although often dismissed as a temporary inconvenience, this condition can significantly affect your daily life if left untreated.
The Hidden Health Signal
Ear pain when swallowing should not be taken lightly, as it may be a hidden signal of an underlying health condition. Our bodies are intricate systems where seemingly unrelated symptoms can often be interconnected. We can detect and prevent serious issues by paying attention to these signals and seeking medical advice before they worsen.
Probable Causes of Ear Pain When Swallowing
Let’s explore some of the common causes behind ear pain when swallowing:
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The Eustachian tubes are small passages that connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. When these tubes become blocked or fail to function correctly, it can result in ear pain during swallowing.
Upper Respiratory Infections
Common colds, sinus infections, and other respiratory illnesses can lead to inflammation and congestion, causing ear pain during swallowing.
Tonsillitis
Inflamed tonsils, often caused by bacterial or viral infections, can trigger ear pain when swallowing because of the proximity of the tonsils to the ears.
Swimmer’s Ear
Also known as otitis externa, this condition occurs when water remains trapped in the ear canal, leading to infection and ear pain during swallowing.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorder
Problems with the TMJ, which connects your jawbone to your skull, can radiate ear pain, especially when swallowing.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Acid reflux or GERD can cause stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, irritating the throat and leading to ear pain when swallowing.
Inflammation of the Middle Ear
Infections or inflammations of the middle ear, such as otitis media, can cause ear pain that intensifies during swallowing.
Dental Issues
Dental infections, tooth abscesses, or affected wisdom teeth can cause referred pain, manifesting as ear pain when swallowing.
Allergies
Allergic reactions or hay fever can lead to nasal congestion and subsequent ear pain when swallowing.
Foreign Body
In rare cases, a foreign object lodged in the ear or throat can cause localized pain during swallowing.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying the underlying cause of your ear pain when swallowing requires careful observation and a medical evaluation. Alongside ear pain, you may experience additional symptoms such as:
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Jaw or neck pain
- Fever or chills
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can conduct a thorough examination and determine the root cause of your discomfort.
During your medical evaluation, your doctor may:
- Conduct a detailed medical history interview to identify potential triggers or underlying conditions.
- Perform a physical examination, including an examination of the ears, nose, and throat.
- Order diagnostic tests such as a throat culture, blood tests, imaging (e.g., X-rays or CT scans), or referral to a specialist if necessary.
The information gathered through these assessments will help make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan.
Remedies and Relief for Ear Pain When Swallowing
While medical intervention is often necessary to address the underlying cause of ear pain when swallowing, you can try several remedies and self-care techniques at home to alleviate your symptoms. Here are some suggestions:
- Stay Hydrated: Maintaining hydrated can help thin mucus and reduce throat and ear irritation.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress or heating pad to the affected ear can help ease pain and reduce inflammation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can temporarily relieve ear pain and reduce inflammation. However, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider before taking any medications, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are currently taking other medications.
- Saltwater Gargles: Mixing a teaspoon of salt in warm water and gargling with it can help soothe your throat, reducing associated ear pain.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of smoke, allergens, and other irritants that can further inflame your throat and exacerbate your symptoms.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water or using a humidifier can help alleviate congestion and relieve ear pain caused by upper respiratory infections.
- Proper Dental Care: Maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and addressing dental issues promptly can help prevent referred ear pain because of dental problems.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: If you suspect that acid reflux or GERD may contribute to your symptoms, try avoiding trigger foods such as spicy or acidic foods, caffeine, and carbonated beverages.
It’s important to note that while these remedies may provide temporary relief, they may not address the root cause of your ear pain when swallowing. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for a proper diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Seeking Professional Help
While home remedies and self-care practices can provide temporary relief, addressing the underlying cause of your ear pain when swallowing is crucial. A healthcare professional can offer a more accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options based on your condition and medical history. These may include:
- Prescription medications such as antibiotics to treat infections or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Ear drops to alleviate discomfort and inflammation.
- Referral to an ear, nose, and throat specialist (otolaryngologist) for further evaluation or specialized treatment.
Remember, each individual is unique, and the treatment plan will be tailored to your needs. Early intervention and proper medical care can help alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and prevent potential complications.
Treatment for ear pain when swallowing
Treatment for ear pain when swallowing depends on the underlying cause. Consulting with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan is essential. Here are some potential treatments that may be recommended:
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction:
- Nasal decongestants or corticosteroid nasal sprays reduce inflammation and open up the Eustachian tubes.
- Auto-inflation techniques, such as the Valsalva maneuver or swallowing while pinching the nose and blowing gently, help equalize ear pressure.
Upper Respiratory Infections:
- Rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers to manage symptoms.
- Prescription medications, such as antibiotics for bacterial infections or antivirals for viral infections.
- Nasal decongestants or saline nasal sprays to relieve congestion.
Tonsillitis:
- Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, warm saltwater gargles, and throat lozenges to alleviate symptoms.
- In severe or recurrent cases, surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) may be recommended.
Swimmer’s Ear:
- Prescription ear drops containing antibiotics or antifungal medications to treat the infection.
- Avoid swimming or excessive moisture exposure until the infection resolves.
- Keeping the ear dry and clean.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorder:
- Self-care measures include applying warm compresses, practicing stress-reduction techniques, and avoiding excessive jaw movements.
- Physical therapy or exercises to improve jaw mobility and alleviate pain.
- Mouth guards or oral splints to reduce teeth grinding or clenching.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
- Lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications (avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals), weight management, and head elevation while sleeping.
- Medications such as antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors to reduce stomach acid production and manage reflux symptoms.
- In severe cases, surgical interventions may be considered.
Inflammation of the Middle Ear:
- Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections.
- Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, alleviate discomfort.
- Warm compresses soothe the affected ear.
- Sometimes, a myringotomy (small incision in the eardrum) may be necessary to drain fluid or relieve pressure.
It is important to note that these treatments are general suggestions and may vary based on individual circumstances. The specific treatment approach will depend on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. Follow your healthcare provider’s advice for the most appropriate treatment for your condition.
Prevention and Self-Care
While it’s not always possible to prevent ear pain when swallowing, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. These include practicing hygiene to prevent infections, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing chronic conditions like GERD.
If you’re currently experiencing ear pain when swallowing, there are a few things you can do at home to help manage your symptoms. These include taking over-the-counter pain relievers, using a warm compress on the affected ear, and staying hydrated to help keep your throat moist.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is ear pain when swallowing a severe condition? A: While various factors can cause ear pain when swallowing, it is essential not to ignore persistent or worsening symptoms. Seeking medical advice can help determine the severity of your condition and guide you toward appropriate treatment.
Q: Can allergies cause ear pain when swallowing? A: Yes, allergies can contribute to nasal congestion and inflammation, leading to ear pain when swallowing. Allergy management and treating underlying allergic rhinitis can often alleviate associated symptoms.
Q: When should I consult a doctor about my ear pain when swallowing? A: If your ear pain when swallowing persists for more than a few days, is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, or significantly affects your daily life, it is advisable to seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
Ear pain when swallowing should not be disregarded as a mere inconvenience. It can be a hidden signal of an underlying health issue that requires attention and care. You can find relief and prevent potential complications by understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate medical help. Don’t let ear pain hinder your quality of life—take action and prioritize your well-being. Early intervention is critical to resolving discomfort and promoting optimal ear and throat health.
Reference
https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/hearing-ear-infections-deafness
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322129

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.