An Insightful Guide to Eye Cancer: Causes to Prevention
Discover comprehensive insights on eye cancer, from its causes and symptoms to proactive prevention measures. Stay informed and protect your vision effectively.
Key Takeaways:
| Introduction | |
| What is it? | |
| Causes | |
| At Risk | |
| Early Signs | |
| Symptoms
Signs Photos Treatment Prevention FAQs Conclusion
|
Introduction
Eye cancer is a concerning, albeit rare, disease. Like other forms of cancer, early detection is crucial for effective treatment and better outcomes. This guide seeks to educate its readers about what eye cancer is, its various types, causes, risk factors, and signs. Armed with this knowledge, individuals are better placed to seek timely medical intervention should they suspect they’re exhibiting symptoms of this disease.
What is Eye Cancer?
It refers to the abnormal growth of cells in or around the eye, which can lead to malignancies. These malignancies can manifest in various forms and affect different parts of the eye. Understanding eye cancer is pivotal for both preventing it and seeking timely treatment.
Types of Eye Cancer
Eye cancers can be primarily categorized based on the area of the eye they affect. Here’s a brief outline:
- Uveal Cancer: The most common type, it primarily affects the iris, ciliary body, or choroid.
- Retinoblastoma: A rare form mostly affecting children, originating in the retina.
- Conjunctival Cancer: Originates in the conjunctiva, the thin membrane covering the front of the eye and inner eyelids.
| Type | Area Affected | Common Age Group |
| Uveal Cancer | Iris, Ciliary Body, Choroid | Adults |
| Retinoblastoma | Retina | Children |
| Conjunctival Cancer | Conjunctiva | Adults |
What Causes Eye Cancer?
The exact cause of eye cancer isn’t always clear, but some known factors include:
- Excessive sun exposure
- Genetic predispositions
- Certain eye conditions and diseases
Each type of eye cancer may have specific contributing factors. Further research is necessary to uncover more about these causes.
Who is at Risk?
Individuals may be at higher risk for eye cancer based on the following factors:
- Age: Older adults are generally more susceptible.
- Ethnicity: People with fair skin may have a higher risk.
- Genetics: A family history of eye cancer increases risk.
What are the First Signs of Eye Cancer?
Early signs can be subtle and include:
- Changes in vision
- Seeing floaters or flashes
- Visible growth in the eye
Being vigilant about these early signs can lead to early diagnosis and treatment.
What Does Eye Cancer Look Like?
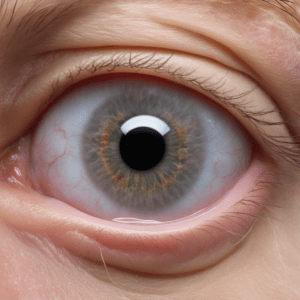
Eye cancer’s appearance can vary widely based on the type and stage of cancer. Common indications include a visible growth in the eye, a change in the color of the iris, or a dark spot on the iris or conjunctiva.
Symptoms
Beyond the physical appearance, symptoms can include:
- Loss of vision
- Eye pain or redness
- Bulging of one eye
It’s essential to consult with an eye specialist if you experience any of these symptoms persistently.
Signs of Eye Cancer
Eye cancer’s signs are synonymous with its symptoms. The difference is, that symptoms are experienced by the patient, while signs are observed by the medical practitioner. Early detection is vital, hence the importance of regular eye check-ups.
Photos
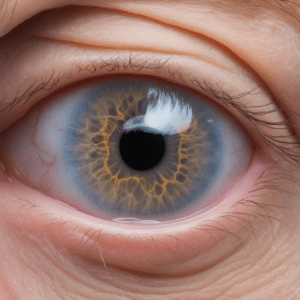
Photographs can help in understanding how eye cancer manifests visually. Many medical platforms provide images of eye cancer, but a discussion with a healthcare provider is essential for a correct diagnosis and understanding.
| Type | Common Visual Signs |
| Uveal Cancer | Dark spot on iris, change in eye shape |
| Retinoblastoma | Whitish glow in pupil, misaligned eyes |
| Conjunctival Cancer | Pink or red growth on conjunctiva |
Understanding eye cancer through images can provide a clearer picture, but early medical intervention is the key to tackling this disease effectively.
Eye Cancer Treatment
The management and treatment of eye cancer are quite diverse and often depend on the type and stage of cancer. Early detection remains a crucial part of ensuring a successful treatment outcome. Here are common treatments used in managing eye cancer:
Surgery
Surgical removal of the tumor is often the first line of treatment. There are different surgical techniques, and the choice of method depends on the location and size of the tumor.
- Enucleation: Removal of the eye, typically done when the tumor is large.
- Eye Wall Resection: Removal of a part of the eye wall for smaller tumors.
Radiation Therapy
This involves using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Types include:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Directed at the eye from a machine outside the body.
- Plaque Brachytherapy: A small radioactive disc is placed directly on the eye near the tumor to deliver radiation.
| Treatment | Description | Typical Usage |
| Surgery | Removal of tumor | Large/small tumors |
| Radiation Therapy | Killing cancer cells | Localized tumors |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be used in conjunction with other treatments to eradicate cancerous cells.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy:
These newer treatment options target specific characteristics of cancer cells or boost the immune system to fight cancer.
Laser Therapy:
Laser therapy employs high-intensity light to destroy cancer cells. It’s less invasive and often used for smaller tumors or in conjunction with other treatments.
Eye Cancer Prevention and Tips to Protect Your Eyes
Preventing eye cancer entirely might not be possible due to its complex nature and potential genetic links. However, there are steps one can take to minimize risks and protect eye health:
- Regular Eye Examinations:
- Have your eyes checked by an eye specialist annually.
- Early detection of any abnormalities can lead to early treatment.
- Sun Protection:
- Wear sunglasses with UV protection.
- Avoid direct sun exposure, especially during peak sun hours.
- Healthy Lifestyle:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Know Your Family History:
- Understand your family’s eye health history.
- If eye cancer runs in the family, get regular screenings.
- Practice Eye Safety:
- Wear protective eyewear during activities that could lead to eye injury.
- Ensure a safe working environment to prevent eye hazards.
Taking these preventive measures can significantly lower the risks associated with eye cancer and other eye-related diseases. It’s essential to foster a dialogue about eye health within communities to promote early detection and prevention.
In conclusion, eye cancer, though rare, requires prompt attention and a thorough understanding to manage effectively. With advancements in medical technology, numerous treatment options are available, making early detection and treatment more accessible and efficient. By adopting a preventative approach towards eye health, individuals can mitigate the risks and promote better eye health within their communities.
FAQs
What are the first signs of eye cancer?
The first signs of eye cancer can vary, but some common ones to watch for include:
- Vision Changes: If your vision becomes blurry or distorted, it could be a sign.
- Floaters: Sudden appearance of spots or floaters in your vision.
- Eye Pain: Persistent, unexplained eye pain or discomfort.
- Redness: Frequent redness or irritation that doesn’t go away.
- Changes in Eye Shape: Noticeable changes in the shape or size of your eye.
If you notice any of these signs, seeing a doctor for a check-up is crucial.
Is eye cancer curable?
The curability of eye cancer depends on various factors, including the type of cancer, its stage, and when it’s detected. Some forms of eye cancer, especially if caught early, can be treated successfully. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or other specialized treatments. However, the outcome varies from person to person. Early detection and prompt treatment generally improve the chances of a positive outcome.
What age does eye cancer start?
It can affect individuals of all ages, from infants to the elderly. The age at which it starts depends on the specific type of eye cancer. For example, retinoblastoma, a type of eye cancer, typically affects young children. On the other hand, other forms of eye cancer may be more common in adults, especially as they get older. Regular eye check-ups can help detect eye cancer at any age.
Can people survive eye cancer?
Yes, many people can survive eye cancer, especially when it’s diagnosed early and treated appropriately. The survival rate depends on factors such as the type of eye cancer, its stage, and the chosen treatment. For instance, retinoblastoma in children often has a high survival rate when detected early and treated. However, following your doctor’s recommendations, attending regular follow-up appointments, and maintaining a positive outlook throughout the treatment journey are essential. Early detection and advances in medical care have significantly improved the chances of survival for individuals with eye cancer.
Key Takeaway
Eye cancer, though uncommon, can have severe consequences if not addressed promptly. Knowing its early warning signs is crucial for timely detection and effective treatment. Keep your eyes healthy by staying educated, having regular eye exams, and consulting a healthcare professional at the first sign of any eye irregularities.
Conclusion
Our eyes are our gateway to the magnificent sights around us, making it vital to keep them in good health. While eye cancer is rare, its effects can be drastically life-changing. Having a good understanding of what it entails, being vigilant about noticing any unusual signs, and getting early treatment can significantly help in protecting our eyesight. This way, we can continue to explore the beauty of the world through clear vision. It’s a collective duty to prioritize and uphold our eye health.

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.