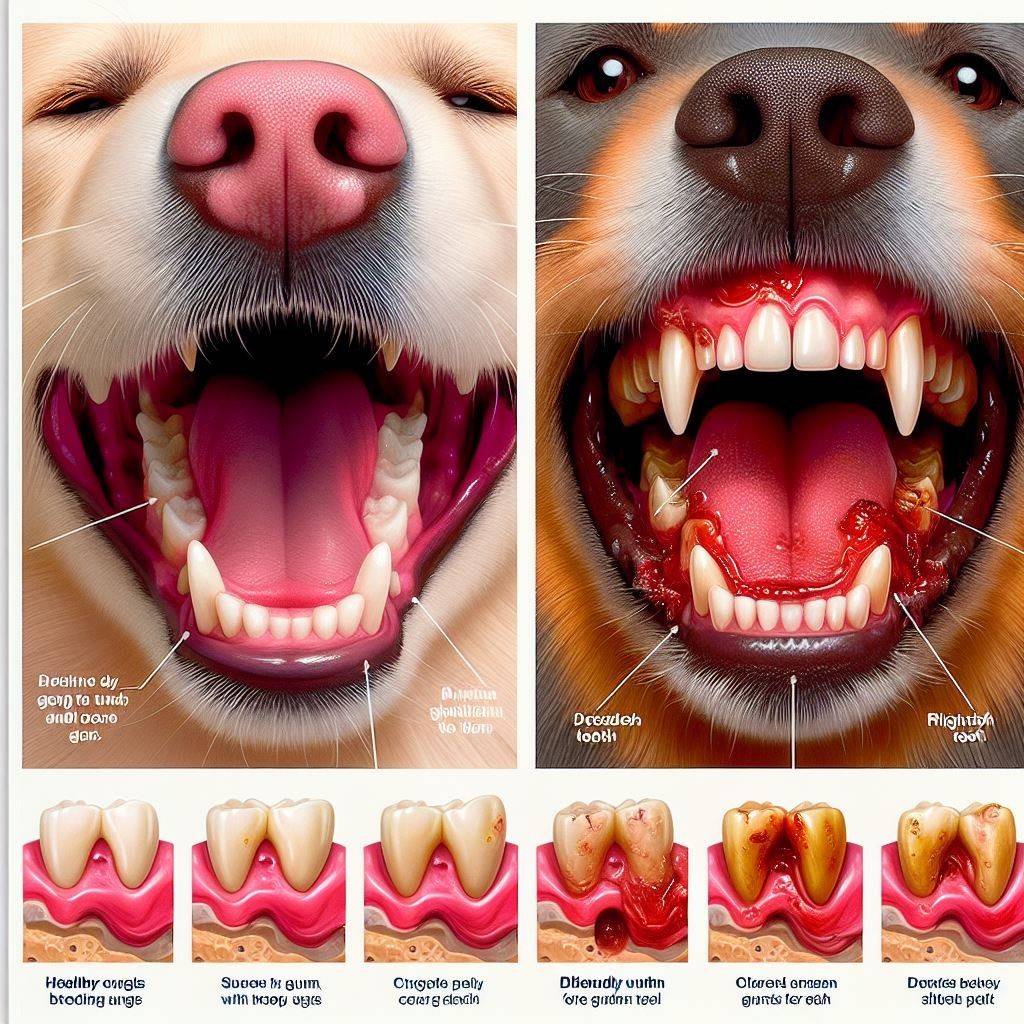
Healthy Dog Gums vs Unhealthy: The Secret Signals You Must Know!
Explore the vital signs in our guide, “Healthy Dog Gums vs Unhealthy: The Secret Signals You Must Know!” Decode your dog’s oral health for optimal pet wellness.
Key Takeaway: healthy dog gums vs unhealthy
- Healthy dog gums are pink, firm, and free of inflammation, while unhealthy gums turn red, swollen, or discoloured, signalling periodontal disease.
- Regular teeth brushing, dental treats, fresh food, and annual vet cleanings maintain good gum health.
- Bad breath, sensitive or bleeding gums, yellow buildup, receding gums, and tooth loss indicate unhealthy gums requiring treatment.
- Left untreated, bacteria from gum infection spreads through the bloodstream, endangering major organs over time.
- Professional dental cleanings treat advanced cases, but daily brushing and limiting sugary foods prevent gum disease from developing.
Healthy Dog Gums vs Unhealthy: Learn how regular gum checks unveil your pet’s overall health. Healthy gums are bubblegum pink, firm, and free from swelling. Unhealthy gums show colour changes, swelling, and bleeding—signs of infection. Recognizing these distinctions empowers pet owners to seek prompt veterinary care. Consistent dental care and professional cleanings minimize infection risk, ensuring your dog enjoys vibrant, healthy gums for years.
What Do Healthy Dog Gums Look Like?
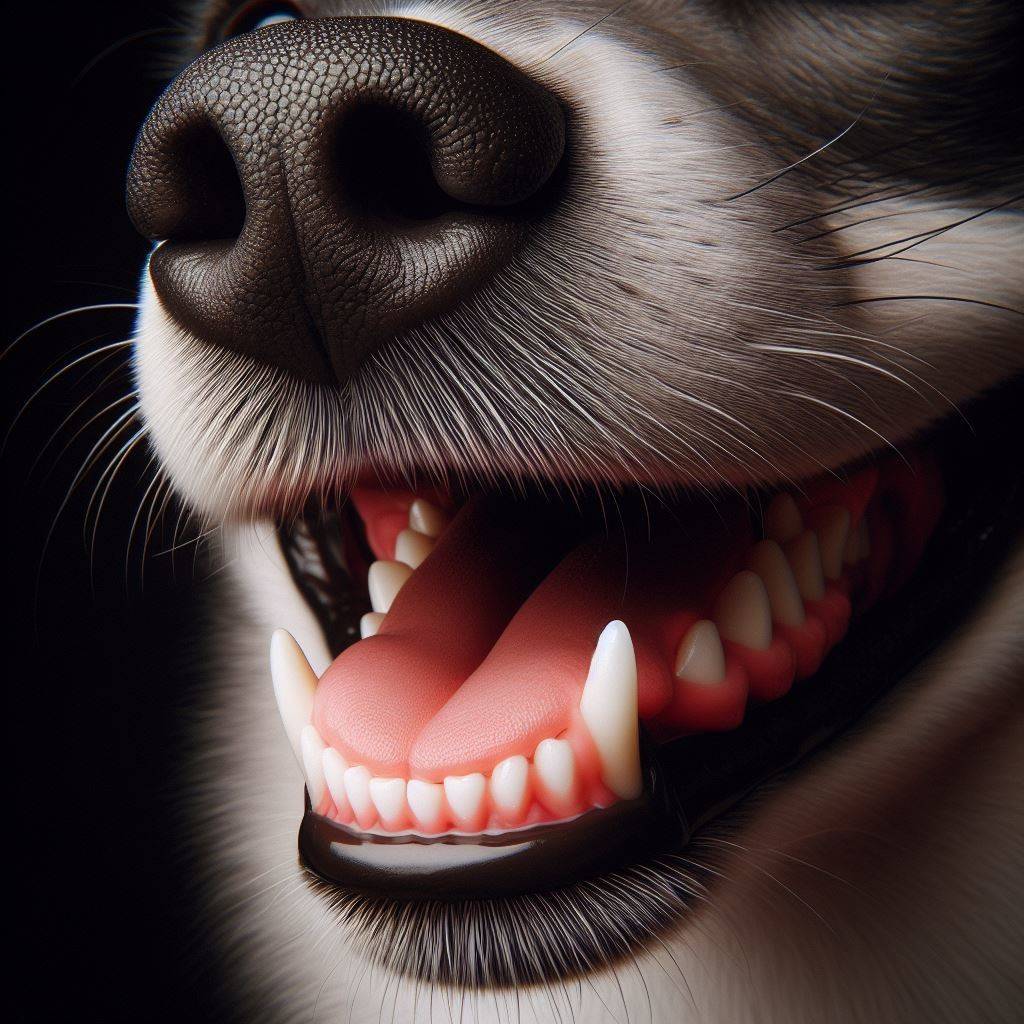

In a dog with good dental health, gums appear:
- Pink– Healthy dog gums sport a bubblegum or salmon pink tone across the gumline. The faded colour indicates mild inflammation.
- Firm & Resilient Texture– When touched, gums feel firm yet flexible and bounce back instantly when released. Boggy, swollen gums demonstrate infection.
- Free of Inflammation or Swelling– No puffy, inflamed areas are visible. Swollen gums flare out from between teeth with a smooth, taut texture.
- Hugs Tooth Tightly– Gums hug the tooth tightly rather than receding or detached. As the infection progresses, the gums pull back, exposing sensitive root areas.
- No Discomfort When Touched– Your dog shows no reaction sensitivity when touching gums, indicating comfort and health. Pain and bleeding signal problems.
Signs of Healthy Dog Gums |
|
| Bright Pink Color | Firm, Flexible Texture |
| No Swelling | Tightly Hugs Tooth |
| No Sensitivity | Resilient When Touched |
Regularly examining teeth and gums lets one notice subtle changes promptly to prevent significant dental disease.
Comparison between Healthy dog gums vs unhealthy
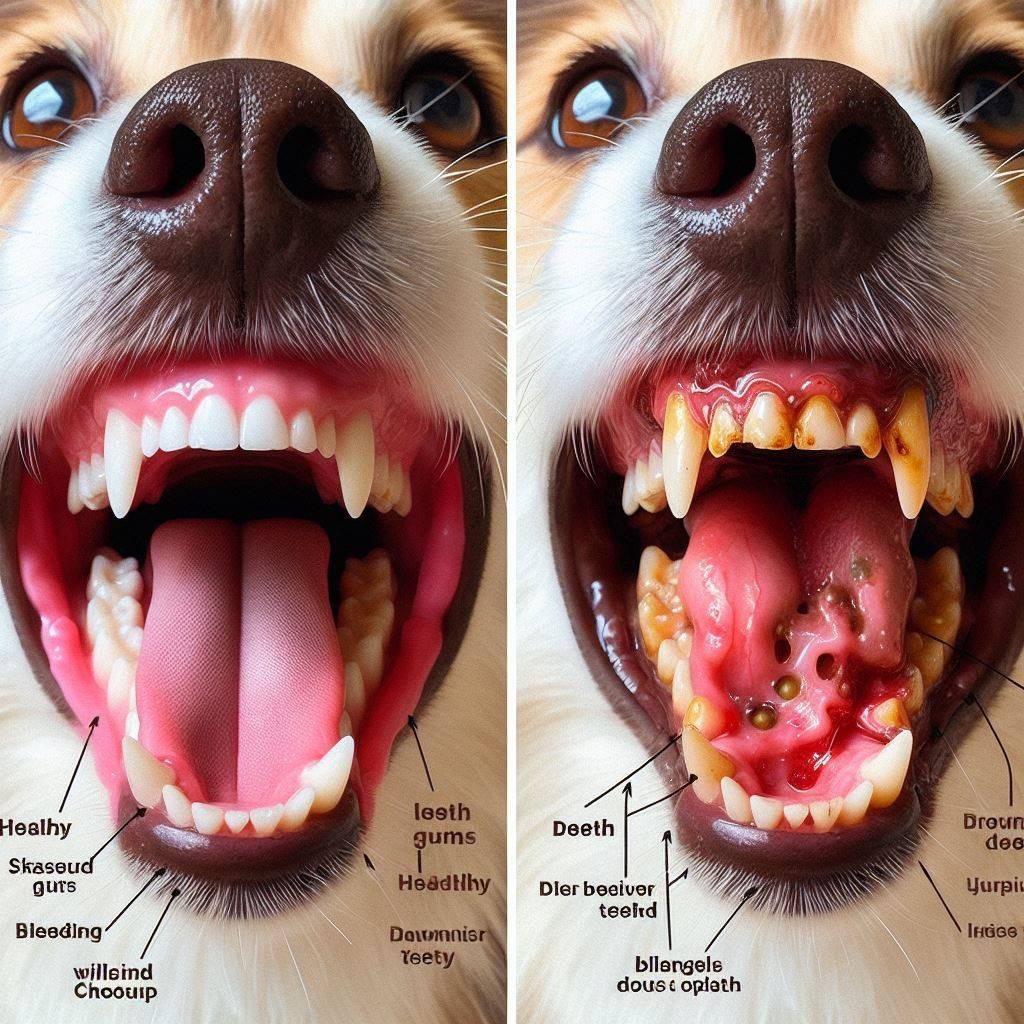
Here is a helpful comparison table outlining the key differences between healthy dog gums and unhealthy dog gums:
| Healthy Dog Gums | Unhealthy Dog Gums | |
| Color | Pink or light red | Bright red, purple/blue, or white |
| Texture | Firm and resilient | Swollen or receding |
| Bleeding | None | Bleeds easily, even with minimal contact |
| Buildup | Little or no tartar/plaque | Heavy tartar or plaque accumulation |
| Attachment | Tightly hugs teeth | Detached from teeth or receding |
| Odor | Normal clean breath | Persistent bad breath |
| Comfort | No reaction to touch | Sensitive or painful response |
| Teeth Condition | Secure with no looseness | Loose or missing teeth |
| Overall Health Impact | Low | Can spread infection to organs over time if left untreated |
The key takeaway in examining your dog’s gums and teeth regularly is to watch for changes in colour, texture, bleeding, gum detachment, and plaque buildup, as these all indicate the development of dental diseases requiring veterinary attention. Catching problems early vastly improves outcomes.
What Do Unhealthy Dog Gums Look Like?
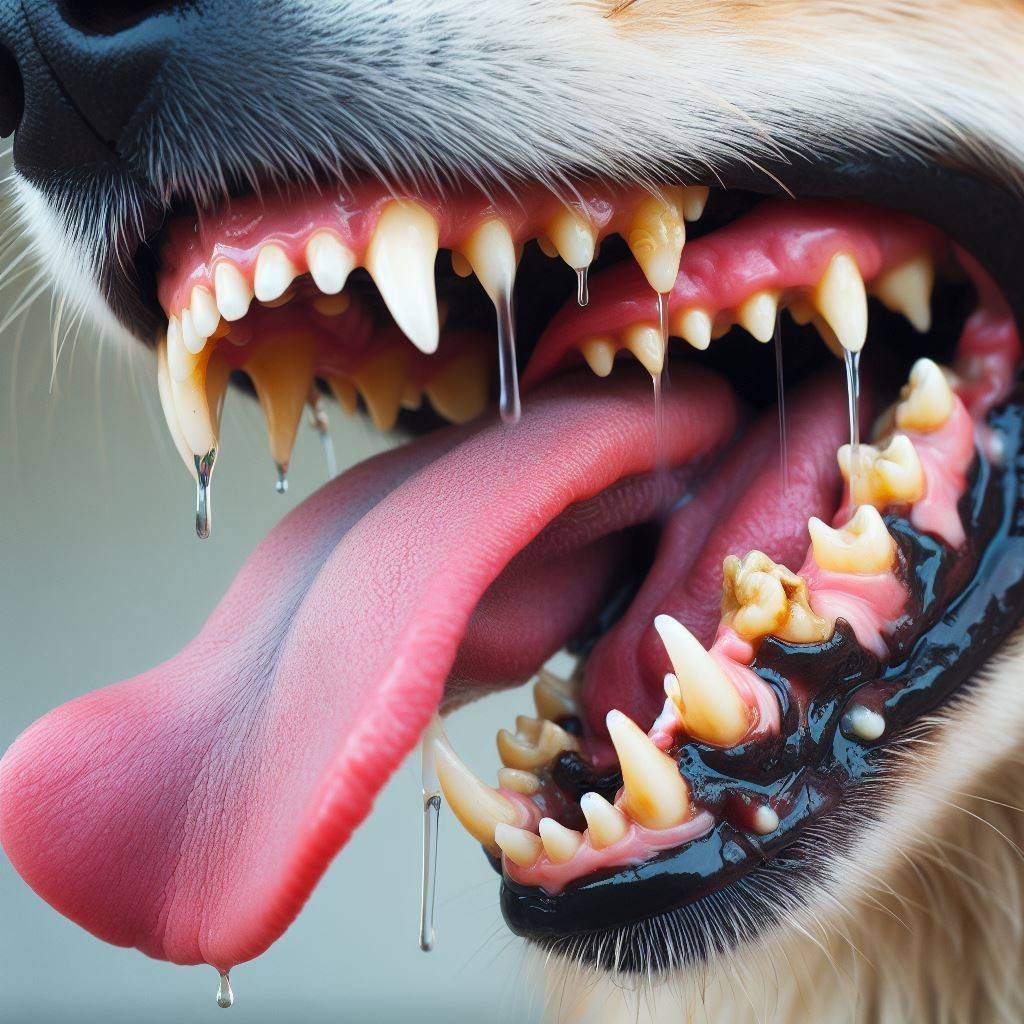

Unhealthy infected gums demonstrate:
- Red or Deep Red Color– Gums fade from pink to red as inflammation progresses. Deep pocket infections flare angry red.
- Swollen Texture– Gums grow puffy and swollen between teeth from inflammation and bacterial accumulation underneath.
- Bleeds Easily– Gentle touch leads to bleeding as infection erodes gum connections.
- Receding Gumline– Gums detach and pull back from teeth, exposing sensitive root areas and erosion.
- Loose Teeth– With the supportive bone structure damaged from infection, teeth eventually loosen or fall out.
- Bad Breath & Debris– Foul breath comes from tartar and bacteria buildup on the gumline and teeth as the disease advances.
Symptoms of Unhealthy Dog Gums |
|
| Fades from Pink to Red | Puffy, Swollen Texture |
| Bleeds with Gentle Touch | Receding Gumline |
| Loose Teeth | Bad Breath |
If left unaddressed, rapid gum deterioration leads to exponential oral pain and systemic health risks.
Why Do Unhealthy Gums Matter?
Unhealthy infected gums don’t just cause oral pain but, over time, allow harmful bacteria to spread into the bloodstream to vital organs.
- Heart, liver, and kidney disease risks grow from sustained oral infection due to bacteria entering the bloodstream.
- Bacteria accumulation in gum pockets eats away tooth-supporting bone, leading to looseness or loss.
- Left untreated, advanced periodontal disease requires complete mouth tooth extraction for relief.
- Poor nutrient absorption from dental pain limits the vital nutrition dogs require.
- Toxic bacteria compromise immune health, making dogs prone to illnesses overall.
While lousy breath or yellowed teeth commonly get dismissed as cosmetic issues, Healthy Dog Gums vs Unhealthy shows that infected bleeding gums represent brewing systemic disease requiring urgent veterinary dental care. Catching gum deterioration early, when still reversible, makes all the difference for dogs’ welfare.
What Causes Unhealthy Dog Gums?
Gum disease stems largely from plaque and tartar buildup, inflaming tissue and proliferating infection in pockets around the teeth and roots.
Plaque & Tartar Causes
- Bacteria accumulation from infrequent brushing and dental care
- Sugary Treats – Carbohydrates and sugars feed bacteria growth
- Poor Hydration – Reduced saliva flow allows more bacteria to thrive
- Genetic Predisposition – Some breeds tend toward gum disease
Usually, plaque forms first but quickly hardens into tartar within days, adhering firmly to teeth. As more layers accumulate, inflamed swollen gums start detaching from teeth, allowing pockets to be subject to infection. Once advanced periodontal disease sets in, professional dental cleanings become necessary to remove substantial buildup and restore health.
How to Prevent Unhealthy Dog Gums
Stopping plaque before it converts to rigid tartar is central to defending against gum disease through these daily practices:
- Brush Teeth 2-3 Times Weekly– Regular brushing removes sticky plaque before it hardens into tartar. Use dog-safe toothpaste and brush all sides.
- Offer Raw Bones for Chewing– Gnawing cleans teeth and builds healthy gums. Look for softer Fitz Factory bones.
- Dental Treats & Chews– Oral hygiene chews use enzymes to hinder tartar and scrub teeth.
- Dental Food/Kibble– Some lines claim patented textures and clean chewing; they have fluoride and compounds limiting tartar enzymes.
- Fresh Water for Rinsing– Hydrating washes away food debris and sugars where bacteria breed.
- Limit Sugary Foods– Avoid sticky processed treats and people’s food as bacteria feast on carbs and sugars.
- Annual Cleanings– Most dogs require annual dental scaler treatments even with diligent home care. Vets examine the gum pockets for issues.
Prevention Practices |
|
| Brush Teeth | Offer Raw Bones |
| Dental Treats/Chews | Fresh Water Access |
| Limit Sugars | Annual Cleanings |
Combining daily home dental care with professional veterinary cleanings is essential to avoid gum disease and infection leading to tooth loss. Prevention is vastly easier than attempting to reverse advanced periodontal disease.
How to Treat Unhealthy Dog Gums
Rehabilitating severely infected, unhealthy gums requires:
- Professional Dental Cleaning– Vets numb, then scale all plaque/tartar above and underneath gumlines, plus take x-rays revealing issues.
- Antibiotics + Pain Meds– Potent prescription antibiotics fight infection for 2 weeks while pain meds allow eating despite discomfort and swelling.
- Anti-inflammatory medication– Drugs like meloxicam reduce severe inflammation, enabling gums to heal.
- Follow-up Exams– Recheck infected areas in 2 weeks, ensuring infection clearance and gum reattachment before scaling all teeth again.
- Ongoing Prevention– Stepped-up daily dental care at home prevents rapid infection recurrence.
In acute infection cases, tooth extraction becomes necessary if beyond saving. **Healthy Dog Gums vs Unhealthy** emphasizes that diligent cleaning, antibiotics, and pain management in most dogs facilitate gum healing. Combining treatment with amplified home care prevents the rapid resurgence of periodontal disease.
Monitoring Dog Gum Health
Pet owners can implement these practices for optimal gum health:
- Lift Lips for Regular Gum Checks– Note colour, texture, swelling, or receded areas.
- Watch for Bad Breath Changes– A foul smell indicates infection and bacteria proliferation.
- Feel for Tartar Buildup– Especially on back molars. Remove gently with the edge of the fingernail.
- Inspect All Sides of Teeth– Use a flashlight to notice back molar issues.
- Contact Vet at Any Changes– Seek advice whenever gums fade red, swell, or bleed.
Don’t ignore subtle oral health changes as they indicate brewing infection. Being proactive preserves dental health and dogs’ overall welfare.
Conclusion about healthy dog gums vs unhealthy
The visible signals distinguish healthy, vibrant gum tissue from progressive phases of periodontal disease. Knowing what to look for empowers pet owners to seek prompt veterinary intervention when those alarming changes emerge. Pairing attentive daily dental care with professional cleanings has been proven to sustain long-lasting dental health. With vigilance, proactive steps at home, and regular veterinary oversight, dogs’ teeth and gums can remain robust for years.
Recommended reading
Signs of Brain Tumor in Dogs: A Closer Look at Canine Health

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.