The best way to manage High Cholesterol and diabetes
Manage high Cholesterol and Diabetes _ Diabetes and high cholesterol are two of the biggest health problems in the world today. While they are often considered separate issues, research has shown a significant link between them. Having high cholesterol can increase your risk of developing diabetes, and having diabetes can make it more challenging to manage your cholesterol levels.
Understanding the link between high cholesterol and diabetes
is crucial for anyone looking to manage these conditions and reduce their risk of severe health problems like heart disease. In this article, we’ll explore the connection between high cholesterol and diabetes, the risks associated with both conditions and strategies for managing them effectively. By the end, you’ll better understand how these two conditions are related and what you can do to take control of your health.
High Cholesterol and Diabetes: What’s the Connection?
High cholesterol and diabetes share a complex relationship that can challenge managing both conditions. Insulin resistance is a significant component in the relationship between the two conditions. Insulin is a hormone that plays a role in maintaining normal blood sugar levels. In people with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or doesn’t use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Explanation of how high cholesterol and diabetes are linked
High cholesterol and diabetes are linked through various mechanisms, including insulin resistance, lipid imbalances, and the increased risk of developing diabetes associated with high cholesterol levels.
Insulin resistance is a key factor in both conditions.
In people with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or doesn’t use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance can also contribute to high cholesterol levels by triggering the liver to produce more cholesterol. High blood sugar can also hurt the walls of the arteries, which can cause plaque to build up and raise the risk of heart disease.
Lipid imbalances
Triglyceride levels are high, and HDL cholesterol levels are low, which are also common in people with high cholesterol and diabetes. These imbalances can increase the risk of heart disease and other serious health problems. Finally, research has shown that high cholesterol can increase the risk of developing diabetes. The risk of getting type 2 diabetes is higher in those with high LDL cholesterol levels, likely because of impairments in insulin sensitivity and insulin resistance.
Overall, the link between high cholesterol and diabetes is complex and multifaceted. Understanding how these linked conditions can help individuals manage their health more effectively and reduce the risk of serious complications.
The impact of high cholesterol on blood sugar levels

High cholesterol can affect blood sugar levels.
Firstly, high cholesterol levels can lead to insulin resistance,
This can make insulin resistance worse and raise blood sugar levels. This occurs because cholesterol buildup in the cells can interfere with the signalling pathways that allow insulin to transport glucose into the cells.
Secondly, high cholesterol can contribute to the development of inflammation in the body.
It increases the likelihood of acquiring type 2 diabetes and decreases insulin sensitivity. Inflammation can also damage the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, further exacerbating insulin resistance.
And lastly, plaque in the artery walls can form when LDL cholesterol levels are too high.
This can restrict blood flow and impair the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
This can lead to cellular damage and inflammation, further impairing insulin sensitivity and increasing the risk of developing diabetes. Those who suffer from excessive cholesterol should monitor their glucose levels and work with their healthcare provider to manage their cholesterol levels effectively to reduce the risk of developing diabetes and other serious health complications. This may include lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, medication, or other necessary interventions.
Understanding the Risks of High Cholesterol and Diabetes
Understanding the risks of high cholesterol and diabetes is essential for managing these conditions effectively and reducing the risk of severe health complications. High cholesterol levels can lead to a buildup of plaque in the artery walls and other severe cardiovascular conditions, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and other circulatory problems. Also, high cholesterol can contribute to the development of diabetes, as outlined in the previous section.
Diabetes increases the risk of developing various health complications. Nerve damage, renal failure, blindness, and other serious problems can result from high blood sugar levels, damaging the blood arteries and nerves in the body. People with diabetes are also more likely to get heart disease, stroke, and other diseases of the heart and blood vessels. But when both high cholesterol and diabetes are present, the risk of heart disease and other serious health problems increases greatly.
In reality, those with diabetes have two to four times the chance of getting heart disease as those without the condition. This highlights the importance of managing both conditions effectively and addressing any underlying risk factors. Overall, individuals with high cholesterol and diabetes need to work with their healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that includes lifestyle changes, medication, and other interventions as needed. Regular monitoring of cholesterol and blood sugar levels is also essential for managing these conditions effectively and reducing the risk of severe health complications.
Cholesterol causes diabetes-related heart disease.
Health and Fitness
Both high cholesterol and diabetes are significant risk factors for heart disease, and having both conditions can increase the risk even further. High cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the artery walls, narrowing the arteries and reducing blood flow to the heart. This may raise your heart attack or stroke. Blood clots caused by plaque ruptures are another potential source of organ damage. Yet, diabetes may impair the health of the blood vessels and nerves that supply the heart.
Reduced blood supply to the heart increases the likelihood of a heart attack after such an incident. Those with diabetes are also more likely to experience hypertension and high cholesterol, both risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The risk of cardiovascular disease is already elevated among patients with diabetes, and they frequently suffer from additional health issues like obesity or metabolic syndrome. Combining these factors can significantly increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events.
Heart disease is associated with diabetes, high triglycerides, and low HDL cholesterol.
Triglycerides are a type of fat that is found in the blood. Triglycerides tend to be high in people with diabetes, and HDL cholesterol tends to be low. High levels of triglycerides are associated with an increased risk of heart disease, especially in people with low HDL cholesterol or “excellent” cholesterol transports blood cholesterol to the liver for removal. Insulin resistance can raise triglycerides and lower HDL cholesterol in people with diabetes.
This is because insulin resistance can increase the production of triglycerides in the liver and decrease the clearance of these fats from the bloodstream. Additionally, in managing High Cholesterol and diabetes, high levels of triglycerides can lead to a decrease in HDL cholesterol levels.
High triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol increase the risk of heart disease in people with diabetes. Thus, appropriate management of these illnesses by alterations to one’s way of life and, if necessary, medication is crucial in preventing potentially fatal health problems. Patients with diabetes can lower their triglyceride and HDL cholesterol levels by following a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, and controlling their weight.
Statins and fibrates are two medications that can control these disorders and lower the patient’s risk of cardiovascular disease. A personalized treatment plan considering these and other cardiovascular risk factors should be developed in close collaboration with a healthcare professional.
Managing High Cholesterol and Diabetes

Managing high cholesterol and diabetes can be challenging, but it is essential for reducing the risk of severe health complications. Here are some tips for managing these conditions:
1-Follow a healthy diet:
A healthy diet is crucial for managing high cholesterol and diabetes. Eat various fruits, veggies, healthy grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated and trans fats.
2-Exercise regularly:
People with diabetes who work out regularly can improve their cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Thirty minutes of moderate exercise daily, like brisk walking, is recommended most days of the week. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting an exercise program.
3- Maintain a healthy weight:
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing high cholesterol and diabetes. Losing even a handful of weight can improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. If needed, work with your healthcare provider to develop a healthy weight loss plan.
4- Take medication as prescribed:
If changing one’s lifestyle isn’t enough to control high cholesterol and diabetes, medication may be needed. It is essential to take medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider and to attend regular check-ups to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
5- Quit smoking:
People with diabetes or high cholesterol are more likely to get heart disease and other serious health problems if they smoke. If you smoke, talk to your healthcare provider about strategies to quit.
6- Manage stress:
Stress can impact blood sugar and cholesterol levels in people with diabetes. Finding ways to manage stress, such as meditation, yoga, or other relaxation techniques, can help improve overall health. Managing high cholesterol and diabetes is crucial for reducing the risk of severe health complications like heart disease. By following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, taking medication as prescribed, quitting smoking, and managing stress, you can improve your health and reduce your risk of complications. Consult your healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and circumstances.
The role of medication in managing high cholesterol and diabetes
The role of medication is crucial in managing high cholesterol and diabetes. For people with high cholesterol and diabetes, medication is often prescribed besides lifestyle changes. There are several types of medications available that can help manage high cholesterol and diabetes. Stations are a class of drugs that are commonly prescribed for high cholesterol. They work by reducing the production of cholesterol in the liver.
Stations have been demonstrated to minimize the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke in persons with diabetes and decrease cholesterol levels. Another type of medication that may be prescribed for people with high cholesterol and diabetes is fibrates. Fibrates work by lowering triglyceride levels and increasing HDL cholesterol levels.
Besides stations and fibrates, other medications that may be prescribed for people with high cholesterol treatment of diabetes treatment include niacin, bile acid sequestrants, and ezetimibe. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication regimen for managing high cholesterol and diabetes. It is also essential to carefully follow the prescribed medication regimen and to report any side effects or concerns to the healthcare provider
check-ups for optimal health.
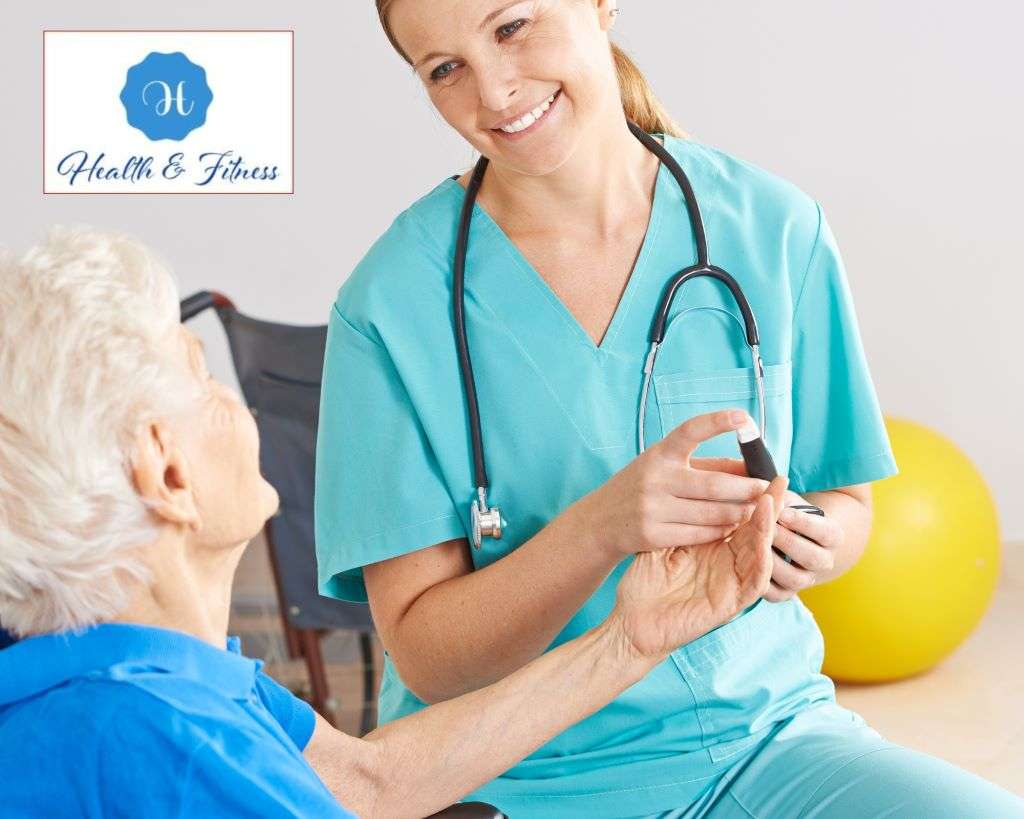

Regular monitoring and check-ups are crucial for people with high cholesterol and diabetes. Monitoring helps to track changes in cholesterol and blood sugar levels and can help identify any potential issues early on. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help ensure that medication regimens work consistently and can be adjusted as needed. For people with high cholesterol and diabetes, it is typically prescribed to have blood tests every three to six months to monitor cholesterol and blood sugar levels. These tests can provide important information about how well medications and lifestyle changes are working to manage these conditions.
Besides regular blood tests, it is also essential to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider. During these appointments, healthcare providers can review blood test results, adjust medication regimens as needed, and provide guidance on lifestyle changes that can help manage high cholesterol and diabetes. Regular monitoring and check-ups are essential to managing high cholesterol and diabetes. By staying on top of these conditions and working closely with a healthcare provider, people with high cholesterol and diabetes can reduce their risk of complications and maintain good health.
Conclusion
Diabetes and high cholesterol raise heart disease risk. Lifestyle adjustments like a nutritious diet, frequent exercise, and medication can help manage both diseases. Managing high cholesterol and diabetes requires regular doctor visits.
Those with high cholesterol and diabetes can improve their health by managing these illnesses and working with a doctor. There are various resources for controlling high cholesterol and diabetes. Talk to a doctor, study reliable health materials, or join a similar-condition support group.
Recommendation
Remember, managing high cholesterol and diabetes requires making healthy choices and working closely with a healthcare provider. By managing both conditions, you can improve your health and reduce your risk of complications.
References
-
-
- American Heart Association. Cholesterol. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/cholesterol
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Diabetes, Heart Disease, and Stroke. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/heart-disease-stroke
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. High Blood Cholesterol: What You Need to Know. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/high-blood-cholesterol
- Mayo Clinic. Cholesterol management: How lifestyle, medications can help. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/in-depth/cholesterol-management/art-20045935
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Managing Diabetes. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/managing-diabetes
-

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.



