Renal Glycosuria: Understanding the Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Explore Renal Glycosuria: Symptoms, Causes, & Treatments – Get insights on Renal Glycosuria causes & treatment options.
Introduction
Renal glycosuria, an uncommon disorder, inhibits the kidneys’ ability to reabsorb glucose from urine into the bloodstream. This can cause excessive glucose levels in the urine despite healthy blood glucose levels.
This causes elevated urine glucose concentrations despite normal blood glucose levels. While it may not always cause significant health problems, it can concern those affected. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of kidney glucose malfunction. It includes its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and potential complications. If you or a loved one has a kidney sugar spill, consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and discuss therapy. Learn about your illness to make better health decisions and treat your symptoms appropriately. Look closely at Renal glucosuria and see what you need to know.
What is Renal Glycosuria?
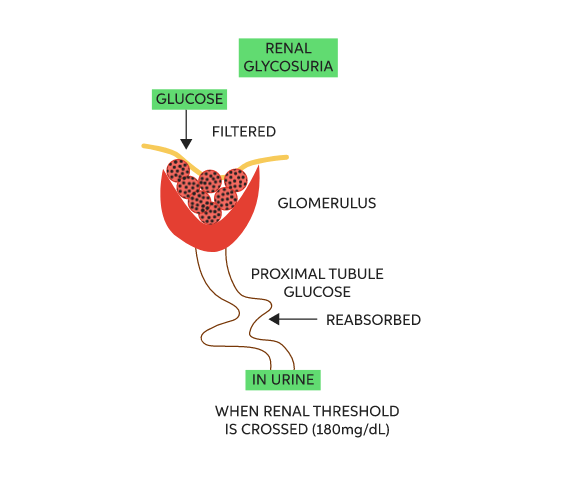
It is a rare hereditary condition that affects glucose reabsorption.
Kidneys filter blood to eliminate waste and excess fluids, including glucose.
They reabsorb glucose into the bloodstream for energy.
Renal glucosuria causes excessive urine glucose levels because of improper glucose reabsorption.
Kidney sugar spill typically has normal blood glucose levels, unlike diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes. The illness may go undiagnosed for years until routine urine testing reveals it. Renal glycosuria is frequently autosomal recessive. The child must inherit the mutant gene from both parents. Occasionally, medicines, infections, or other diseases might cause the syndrome later in life.
Kidney glucose malfunction can lead to urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and other issues.
Hence, kidney glucose malfunction patients should see their doctors regularly.
Symptoms of Renal Glycosuria
It rarely causes symptoms. Most Non-diuretic glycosuria patients have normal blood glucose levels and no diabetic symptoms like thirst, frequent urination, or fatigue.
Kidney glucose malfunction may cause subtle symptoms because of excessive urine glucose.
Symptoms may include:
- Increased urination
Because of high glucose levels in the urine, renal glycosuria patients may urinate more often than those with diabetes.
- Too much thirst.
Sometimes urinating more can make you feel dehydrated and thirsty.
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
Infections from high urine glucose levels can cause urination pain, fever, and lower abdominal pain.
Other disorders besides kidney sugar spill may cause these symptoms. If you have any of these symptoms, see a doctor. Renal glucosuria is usually asymptomatic. However, excessive urine glucose levels might cause minor symptoms.
See a doctor if you suspect Renal glucosuria or have worrying symptoms.
Causes of Renal Glycosuria
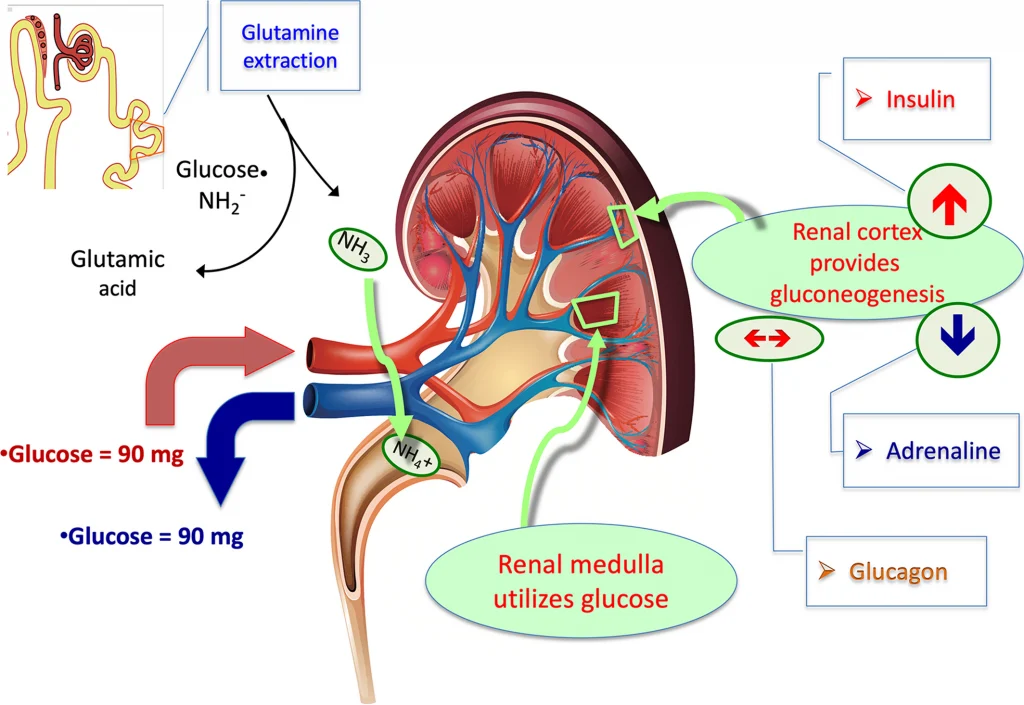
Renal glucosuria is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder that requires both parents to carry the mutant gene.
The kidneys’ glucose reabsorption protein, SLC5A2, is mutated in the disease. In rare situations, drugs, infections, or other illnesses that impair glucose reabsorption might cause renal glycosuria later in life. Diuretics with cidofovir can produce Renal glucosuria.
Pyelonephritis and Fanconi syndrome might cause renal glycosuria.
Acquired Renal glycogen is rare and mostly inherited, but external stimuli can induce it.
Overall, a SLC5A2 gene mutation that decreases urine glucose reabsorption causes renal glucosuria. Acquired renal glycosuria is rarer than genetic.
Diagnosis of Renal Glycosuria
Renal glycosuria is frequently asymptomatic and found through routine urine tests or genetic mutation screening.
Your doctor may order several tests to confirm renal glycosuria.
-
Urine testing
Simple urine tests can detect glucose.
High urine glucose levels show kidney sugar spill without high blood glucose.
. Bloodwork
Blood glucose tests can rule out diabetes mellitus and other causes of glycosuria.
. Genotyping
SLC5A2 gene mutations confirm kidney sugar spill.
To rule out alternative causes of glycosuria, kidney function tests or ultrasounds may be conducted. They diagnose Renal glucosuria using urine, blood, and genetic tests. Your doctor should diagnose and treat familial renal glucosuria if you suspect it.
Treatment Options for Renal Glycosuria
Currently, there is no cure for kidney sugar spills. However, various treatment options can help manage the condition effectively.
These options include:
-
A low-carbohydrate diet
We encourage Renal glucosuria patients to follow a low-carbohydrate diet to lower blood sugar and urine glucose.
-
Regular exercise
Exercise can manage renal glycosuria by lowering blood sugar and improving insulin sensitivity.
-
Medication
We sometimes recommend medication to help control blood sugar and lower urine glucose levels.
Working closely with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the best treatment plan for your needs.
Complications Associated with Renal Glycosuria
Renal glucosuria is usually harmless, but it might cause difficulties.
-
Increased risk of urinary tract infections
Untreated UTIs can cause pain, discomfort, and kidney damage in people with kidney sugar spills.
Renal glucosuria might increase the risk of kidney stones because of glucose in the urine.
-
Risk of developing diabetes mellitus
Kidney sugar spill is not diabetes, although those with it may get it later.
-
Pregnancy problems
Pregnant women with Renal glucosuria may develop gestational diabetes, which can cause issues during pregnancy and delivery.
These problems are rare, yet conceivable. Kidney sugar spills rarely cause serious health issues.
Renal glucosuria requires constant doctor visits and health monitoring to detect and treat complications early.
Living with Renal Glycosuria
Living with Renal glucosuria can be challenging, requiring significant lifestyle adjustments.
However, with proper management, many individuals with Renal glucosuria can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Some tips for living with Renal glucosuria include:
-
Maintaining a healthy diet
Low-carbohydrate diets lower blood sugar and urine glucose.
- Staying active
Regular exercise can manage nondiabetic glycosuria, which improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar.
-
Monitoring blood sugar levels
It is essential to regularly monitor blood sugar levels to ensure they are within a healthy range.
- Working closely with a healthcare provider
Healthcare providers can help develop a personalized treatment plan and monitor the condition over time.
Coping Strategies for Renal Glycosuria
Coping with Renal glucosuria can be challenging, both physically and emotionally.
Some strategies that may help include:
- Joining a support group for individuals with Renal glucosuria
Support groups can provide a sense of community and help individuals connect with others experiencing similar challenges.
-
Working with a therapist
-
- Living with a chronic ailment can be emotionally challenging, but therapy can help people cope.
-
Practicing self-care
Self-care activities such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
-
Educating yourself
Those with Renal glucosuria can learn about the disease and its treatment.
-
Seeking help when needed
Help from a healthcare provider, loved one, or mental health professional.
Conclusion
Renal glycosuria is a rare genetic condition that affects the kidneys’ ability to filter glucose from the blood. Although there is no cure for renal glycosuria, various treatment options can help manage the condition effectively. These options include a low-carbohydrate diet, regular exercise, and medication if necessary. Renal glucosuria patients should consult a doctor to build a treatment plan and monitor their condition. With proper management, many individuals with kidney sugar spills can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Reference
https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/renal-glycosuria/
https://www.omim.org/entry/233100

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.