Wondering what causes high blood pressure after giving birth? Uncover the top 10 reasons and vital information to safeguard your health. Learn more and find out now.
High blood pressure after giving birth is a concern for many new moms. Understanding what causes high blood pressure after giving birth assists you in managing it better and shields your health. In this newsletter, we’ll find out the top motives behind postpartum hypertension, offer smooth suggestions, and answer non-unusual questions.
What Is High Blood Pressure?
Before we discuss what causes high blood pressure after giving birth, let’s clarify what high blood pressure (hypertension) means. Hypertension occurs when the blood force against your artery partitions becomes too robust. Over time, this strain can harm important organs like your coronary heart, kidneys, and brain. For new moms, postpartum hypertension refers specifically to elevated blood pressure that develops after childbirth.
Untreated, it can cause excessive complications, heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. Monitoring and understanding your blood strain is crucial.
What Causes High Blood Pressure After Giving Birth?
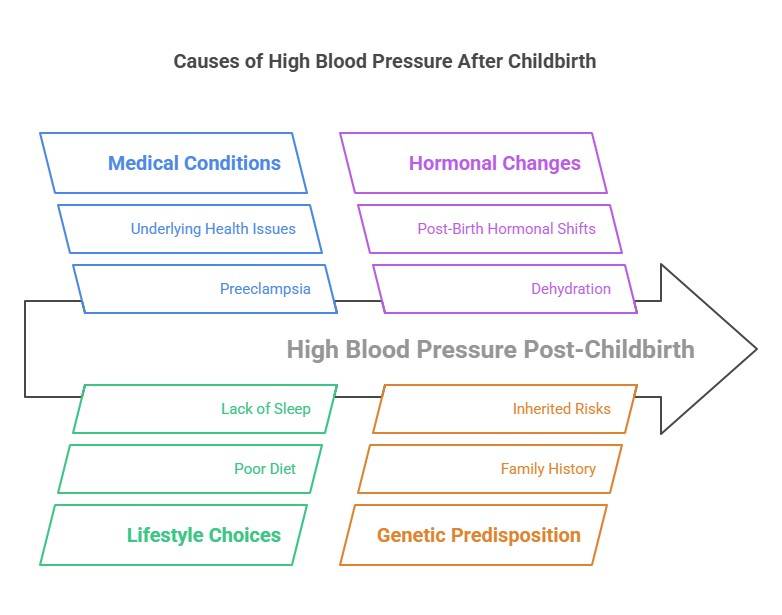
There are several reasons why high blood pressure occurs after childbirth. Below, we’ll discuss the top 10 causes.
1. Preeclampsia That Continues After Delivery
Preeclampsia is a condition where pregnant women develop high blood pressure during pregnancy. Sometimes, preeclampsia doesn’t go away right after delivery. Instead, it can last for weeks or even months afterward. This is one of the major causes of elevated blood pressure post-birth.
Tip: If you have preeclampsia, contact your doctor to monitor your blood pressure. Post-birth hormonal shifts can temporarily increase blood pressure because of changes in progesterone and estrogen levels. Recognize these changes to manage fluctuations.
2. Hormonal Changes Post-Birth
After delivering a baby, your body undergoes dramatic hormonal shifts. Levels of hormones like progesterone and estrogen drop rapidly, which can affect your cardiovascular system. These changes are natural, but they can temporarily increase your blood pressure.
For example, lower levels of progesterone might reduce the relaxation of blood vessels, causing them to constrict and raise blood pressure. Recognizing these postpartum hormonal changes as part of 2. can help you prepare for potential fluctuations.
3. Stress and Anxiety
Being a new mom comes with its own set of challenges: sleepless nights, feeding schedules, and caring for your baby. All this stress can raise your blood pressure temporarily. Persistent stress triggers your body’s “fight or flight” response, which can be harmful to your health over time.
Advice: Try relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga to lower stress levels.
4. Lack of Sleep
Newborns need constant care, which often means less sleep for moms. Sleep deprivation can increase adrenaline production, making your heartbeat faster and raising your blood pressure. Sleep loss is a major trigger for postnatal high blood pressure.
Solution: Ask family members or friends to help so you can catch up on rest. Even brief naps can make a big difference.
5. Dehydration and Its Impact
Breastfeeding requires extra fluids, and dehydration can directly influence what causes high blood pressure after giving birth. When your body doesn’t receive adequate hydration, your blood volume decreases, forcing your heart to work harder to pump blood. This increased effort can raise your blood pressure.
Staying hydrated is simple yet effective. Keep a water bottle nearby and sip frequently throughout the day. If you’re breastfeeding, aim for at least eight glasses of water daily.
6. Poor Diet
Eating unhealthy foods high in salt, sugar, and fat can also lead to high blood pressure. Processed snacks and fast food may seem convenient, but they’re not ideal for your recovery. A poor diet can worsen postpartum cardiovascular risks.
Healthy Swap: Choose whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and low-sodium meals instead.
7. Weight Gain During Pregnancy
If you gain more weight than recommended during pregnancy, losing that weight takes time. Extra pounds put pressure on your circulatory system, increasing your risk of high blood pressure. Managing weight gain is key to reducing postpartum hypertension causes.
Goal: Focus on gradual weight loss by eating balanced meals and staying active within your limits.
8. Underlying Health Conditions
Some medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, or thyroid disorders, can increase the risk of high blood pressure after childbirth. If you have any pre-existing health issues, talk to your doctor about managing them effectively.
Important Note: Regular checkups are key to catching these conditions early.
9. Medications
Certain medications used during labor, such as pain relievers or anesthesia, can temporarily raise blood pressure. Additionally, hormonal contraceptives prescribed after childbirth might affect your blood pressure. Gestational hypertension persistence can sometimes be linked to medication side effects.
Talk to Your Doctor: Always discuss any concerns about medication side effects with your healthcare provider.
10. Genetics
Sometimes, high blood pressure runs out in families. If your parents or siblings have hypertension, you may be at higher risk too. Knowing your family history helps you stay proactive about monitoring your blood pressure.
Prevention Tip: Genetics plays a role, but lifestyle changes can still reduce your risk significantly.
How Can You Prevent Postpartum Hypertension?
While some factors like genetics and preeclampsia are beyond your control, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of high blood pressure after giving birth:
- Consume a balanced diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay hydrated by drinking enough water every day.
- Get regular exercise once your doctor says it’s safe.
- Prioritize self-care and find ways to relax.
- Monitor your blood pressure at home and report changes to your doctor.
Tips for Managing High Blood Pressure After Delivery
Managing high blood pressure after delivery involves a combination of healthy habits and medical guidance. Here are some practical tips:
- Monitor Your Blood Pressure: Keep track of your numbers daily and share them with your doctor.
- Stay Active: Gentle exercises like walking or prenatal yoga can improve circulation.
- Eat Well: Choose foods low in sodium and rich in nutrients.
- Get Support: Lean on family, friends, or support groups to help with childcare and household tasks.
These tips are important because they empower new moms to take charge of their health without feeling overwhelmed.
The Importance of Early Detection
Detecting what causes high blood pressure after giving birth early can prevent complications. Symptoms like headaches, blurred vision, and swelling should never be ignored. If you observe anything out of the ordinary, get in touch with your healthcare provider right away.
Maternal cardiovascular changes after birth can vary from person to person, so personalized care is essential. Regular checkups and open communication with your doctor are vital for ensuring your health remains on track.
FAQs About What Causes High Blood Pressure After Giving Birth
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about postpartum hypertension:
Is experiencing high blood pressure after childbirth typical?
Yes, it’s relatively common for new moms to experience mild increases in blood pressure after childbirth. However, a doctor should always check persistent or severe high blood pressure. Postpartum preeclampsia risks are something to watch out for.
How Long Does Postpartum Hypertension Last?
Postpartum hypertension usually lasts between 6-12 weeks after delivery. For most women, their blood pressure returns to normal during this time. If it doesn’t, further testing may be needed. Monitoring postpartum blood pressure management is crucial.
How Do You Fix Postpartum Hypertension?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Some options include:
- Medication prescribed by your doctor
- Lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and stress management
- Monitoring your blood pressure regularly
Always follow your doctor’s advice for managing your specific situation.
Can Lack of Sleep Cause High Blood Pressure After Giving Birth?
Yes, lack of sleep can contribute to high blood pressure. Sleep deprivation increases cortisol (the stress hormone), which raises blood pressure over time. New parents often struggle with sleep, so finding ways to rest is crucial.
Conclusion: Take Care of Yourself
High blood pressure after giving birth is a concern, but it’s manageable with the right approach. By understanding what causes high blood pressure after giving birth, you can protect your health while enjoying motherhood. Don’t forget, your health is just as important as your baby’s.
Take care of yourself, and congratulations again on your beautiful journey into parenthood!
Final Thoughts
I hope this guide has helped you understand the top reasons behind postpartum hypertension and provided actionable advice. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor if you have concerns. You’ve got this!

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.



