Acid Reflux: 15 Facts About Symptoms, Causes, and Relief Strategies
Discover the signs, symptoms, and effective treatments for acid reflux. Learn how to manage this common condition and improve your quality of life.
Quick Summary
Acid reflux is a common digestive issue where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. Key relief strategies:
- Elevate your head while sleeping
- Avoid trigger foods
- Eat smaller meals
- Lose weight if necessary
- Consider over-the-counter medications
Understanding Acid Reflux: The Basics
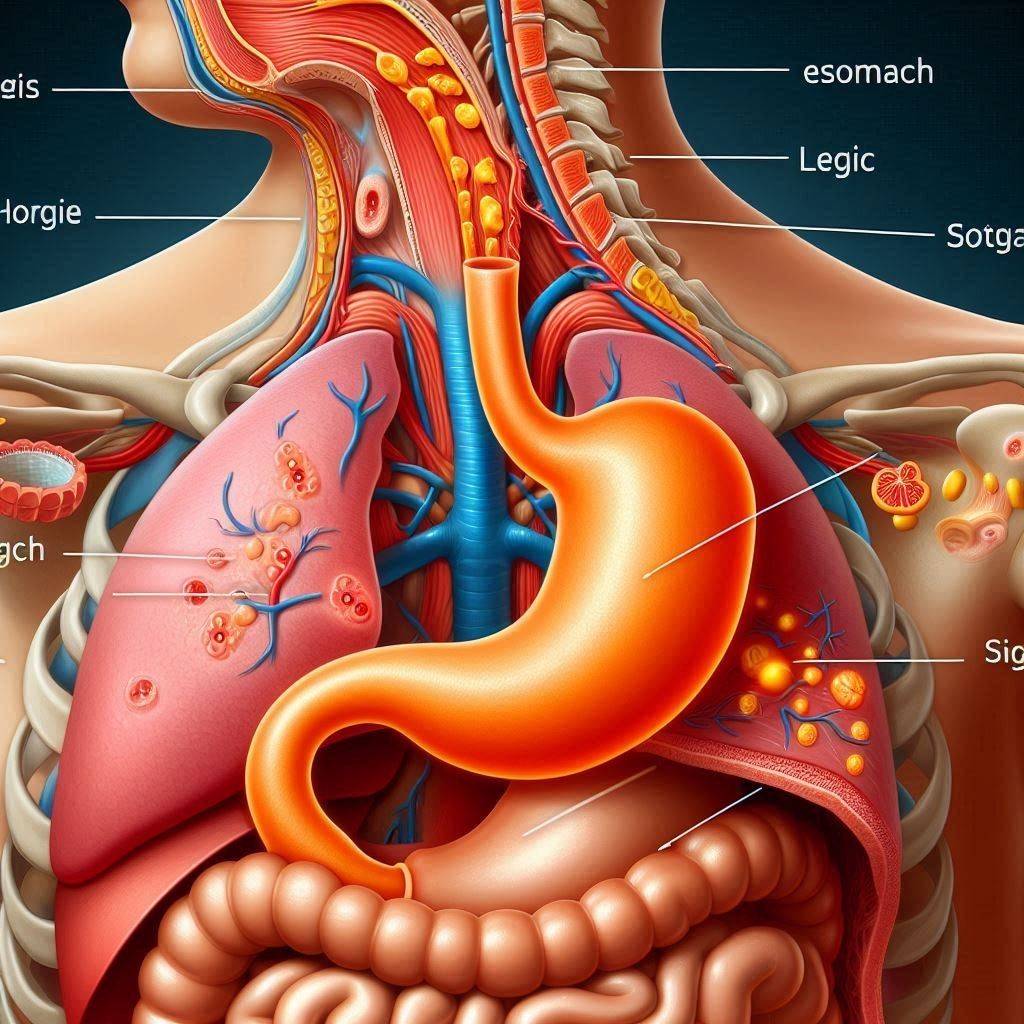
Acid reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) weakens or relaxes inappropriately, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. This can cause a burning sensation in the chest, known as heartburn, along with other uncomfortable symptoms.
I’ve seen many patients struggle with Heartburn, and it’s crucial to understand that while it’s a common condition, it shouldn’t be ignored. Chronic acid reflux can lead to more serious issues if left untreated.
15 Essential Facts About Acid Reflux
Common Symptoms of Acid Reflux
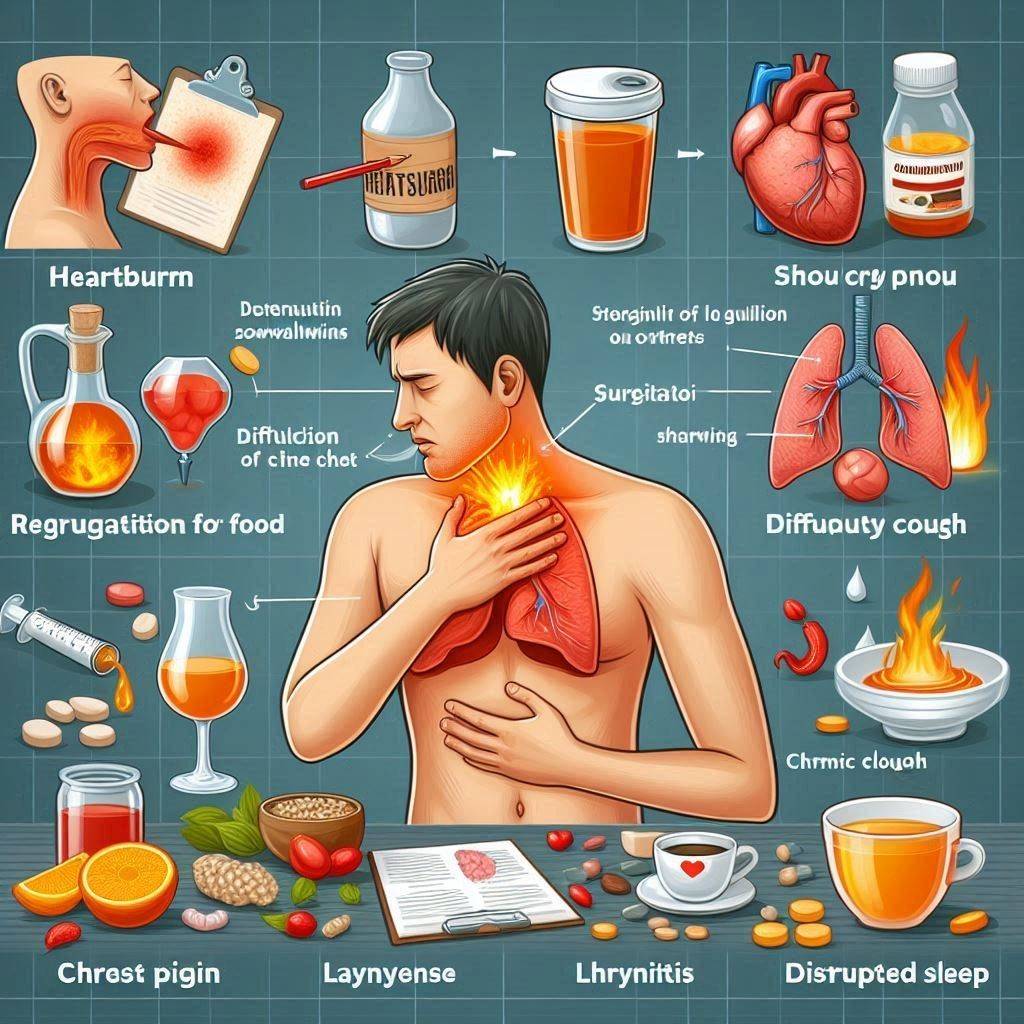
Acid reflux manifests in various ways, and recognizing these symptoms is crucial for proper management:
- Heartburn (a burning sensation in the chest)
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest pain
- The sensation of a lump in your throat
- Chronic cough
- Laryngitis or hoarseness
- Disrupted sleep
In my experience, many patients don’t realize that symptoms like a chronic cough or difficulty swallowing can be related to acid indigestion. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if you’re experiencing these symptoms regularly.
Common Cause and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to or exacerbate acid reflux:
- Obesity or excess weight
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Certain medications (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen)
- Eating enormous meals or lying down right after eating
- Consuming certain foods and drinks (e.g., citrus, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol)
- Hiatal hernia
I’ve noticed that many of my patients are surprised to learn how their lifestyle choices can significantly affect their acid reflux symptoms. Minor changes can often lead to substantial improvements.
The Difference Between Acid Reflux, GERD, and Heartburn
While often used interchangeably, these terms have distinct meanings:
- Acid indigestion: The process of stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus
- GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease): Chronic acid reflux occurring more than twice a week
- Heartburn: A symptom of acid reflux, characterized by a burning sensation in the chest
Understanding these distinctions can help in communicating effectively with your healthcare provider and determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Dietary Triggers and Solutions
Certain foods can trigger or worse acid reflux symptoms:
Triggers to avoid:
- Citrus fruits
- Tomatoes and tomato-based products
- Chocolate
- Mint
- Garlic and onions
- Spicy foods
- Fatty or fried foods
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
Foods that may help:
- Ginger
- Oatmeal
- Bananas
- Melons
- Vegetables (except onions and garlic)
- Lean proteins
I always advise my patients to keep a food diary to identify their triggers. What causes gastroesophageal reflux in one person may not affect another.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Acid Reflux
Simple lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms:
- Elevate the head of your bed by 6-8 inches
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoid lying down for 3 hours after eating
- Quit smoking
- Lose weight if you’re overweight
- Wear loose-fitting clothes
- Practice stress-reduction techniques
I’ve seen remarkable improvements in patients who committed to these lifestyle changes. They often report reduced dependence on medications and improved quality of life.
Over-the-counter medications for Acid Reflux
Several OTC options can provide relief from Peptic reflux symptoms:
- Antacids (e.g., Tums, Rolaids)
- H2 blockers (e.g., Pepcid, Zantac)
- Proton pump inhibitors (e.g., Prilosec, Nerium)
While these medications can be effective, it’s important to use them as directed and consult a healthcare provider for chronic use.
Prescription Treatments for Chronic Acid Reflux
For severe or persistent cases of peptic reflux, prescription medications may be necessary:
- Stronger proton pump inhibitors
- Prokinetics
- Baclofen
In my practice, I’ve found that a combination of prescription medications and lifestyle changes often yields the best results for chronic Reflux esophagitis sufferers.
Natural Remedies for Acid Reflux
Some patients prefer to try natural remedies before or alongside conventional treatments:
- Apple cider vinegar
- Aloe vera juice
- Chewing gum (to increase saliva production)
- Baking soda mixed with water
- Licorice root
- Slippery elm
While some patients report success with these remedies, it’s important to note that scientific evidence for their effectiveness is limited. Always consult with a healthcare provider before trying natural treatments.
Acid Reflux During Pregnancy
Pregnancy often exacerbates or triggers Reflux esophagitis because of hormonal changes and the growing uterus putting pressure on the stomach. Safe management strategies include:
- Eating small, frequent meals
- Avoiding trigger foods
- Sleeping with the upper body elevated
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing
- Discussing safe medication options with your obstetrician
As an obstetrician, I often reassure my patients that while Heartburn during pregnancy can be uncomfortable, it’s usually manageable and resolves after delivery.
Acid Reflux in Infants and Children
Peptic reflux is common in infants because of their immature digestive systems. Symptoms and management differ from adults:
Symptoms in infants:
- Frequent spitting up
- Irritability during or after feeding
- Arching the back while feeding
- Coughing or wheezing
Management strategies:
- Smaller, more frequent feedings
- Keeping the baby upright after feeding
- Thickening breast milk or formula (under doctor’s guidance)
Parents often worry about acid reflux in infants, but I reassure them that it’s usually not a cause for concern and often resolves as the child grows.
Complications of Untreated Acid Reflux
Chronic, untreated, peptic reflux can lead to serious complications:
- Esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus)
- Strictures (narrowing of the esophagus)
- Barrett’s esophagus (precancerous changes to the esophageal lining)
- Esophageal cancer
- Dental erosion
- Chronic cough or asthma
These potential complications underscore the importance of proper peptic reflux management. I always emphasize to my patients that early intervention can prevent these serious outcomes.
When to See a Doctor for Acid Reflux
While occasional Reflux esophagitis is common, certain symptoms warrant medical attention:
- Frequent or severe symptoms that interfere with daily life
- Difficulty swallowing
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Unintentional weight loss
- Chest pain (always rule out cardiac causes first)
- Chronic cough or wheezing
- Signs of bleeding (e.g., vomiting blood, black stools)
I encourage my patients to trust their instincts. If something feels off or symptoms are persistent, it’s always better to get checked out.
Diagnostic Tests for Acid Reflux
To diagnose Reflux esophagitis and rule out other conditions, doctors may use various tests:
- Upper endoscopy
- Esophageal manometry
- Ambulatory pH monitoring
- Barium swallow radiograph
These tests help us understand the severity of the Gastroesophageal reflux and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Acid Reflux and Sleep
It can significantly affect sleep quality. Tips for better sleep include:
- Elevate the head of your bed
- Avoid eating 3 hours before bedtime
- Sleep on your left side
- Use a wedge pillow
- Wear loose-fitting pyjamas
Improving sleep quality can have a profound effect on the overall well-being of Gastroesophageal reflux sufferers. Many of my patients report feeling more energized and experiencing fewer daytime symptoms after implementing these strategies.
Emerging Treatments for Acid Reflux
Research into new acid reflux treatments is ongoing. Some promising areas include:
- Magnetic beads to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter (LINX device)
- Stretta procedure (radiofrequency energy to strengthen the LES)
- Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF)
While these treatments show promise, they’re not suitable for everyone. I always discuss the latest options with my patients to determine the best approach for their cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does acid reflux go away?
Acid reflux can often be managed through a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Key strategies include:
- Identifying and avoiding trigger foods
- Eating smaller meals
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Elevating the head of your bed
- Using over-the-counter or prescription medications as directed by your doctor
- Managing stress
Remember, what works best can vary from person to person, so it may take some trial and error to find the most effective approach for you.
How to reduce gastric reflux?
Reducing gastric reflux involves similar strategies to managing acid reflux:
- Avoid eating large meals, especially close to bedtime
- Stay upright for at least 3 hours after eating
- Quit smoking if you smoke
- Limit alcohol and caffeine intake
- Wear loose-fitting clothing
- Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga
- Consider using antacids or other medications as recommended by your doctor
How to reduce acidity in the stomach?
To reduce stomach acidity:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Avoid acidic and spicy foods
- Stay hydrated
- Chew your food thoroughly
- Try natural remedies like ginger or chamomile tea
- Use antacids when needed
- Consider adding probiotic foods to your diet
- Limit alcohol and caffeine consumption
Does acid reflux ever go away?
It can often be effectively managed with lifestyle changes and medication, leading to significant symptom reduction or even complete resolution in some cases. However, for many people, acid reflux is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management.
Some people may experience temporary acid reflux because of specific circumstances (e.g., pregnancy, certain medications) which can resolve when those circumstances change. In other cases, particularly if lifestyle factors are the primary cause, acid reflux symptoms may go away with appropriate changes in diet, weight management, and other habits.
It’s important to work with your healthcare provider to develop an effective long-term management plan for your acid reflux. Even if symptoms improve or disappear, maintaining healthy habits can help prevent recurrence.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading this comprehensive guide on acid reflux. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you’re better equipped to manage this common condition effectively. Remember, while gastroesophageal reflux can be uncomfortable and disruptive, it’s usually manageable with the right approach. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.



