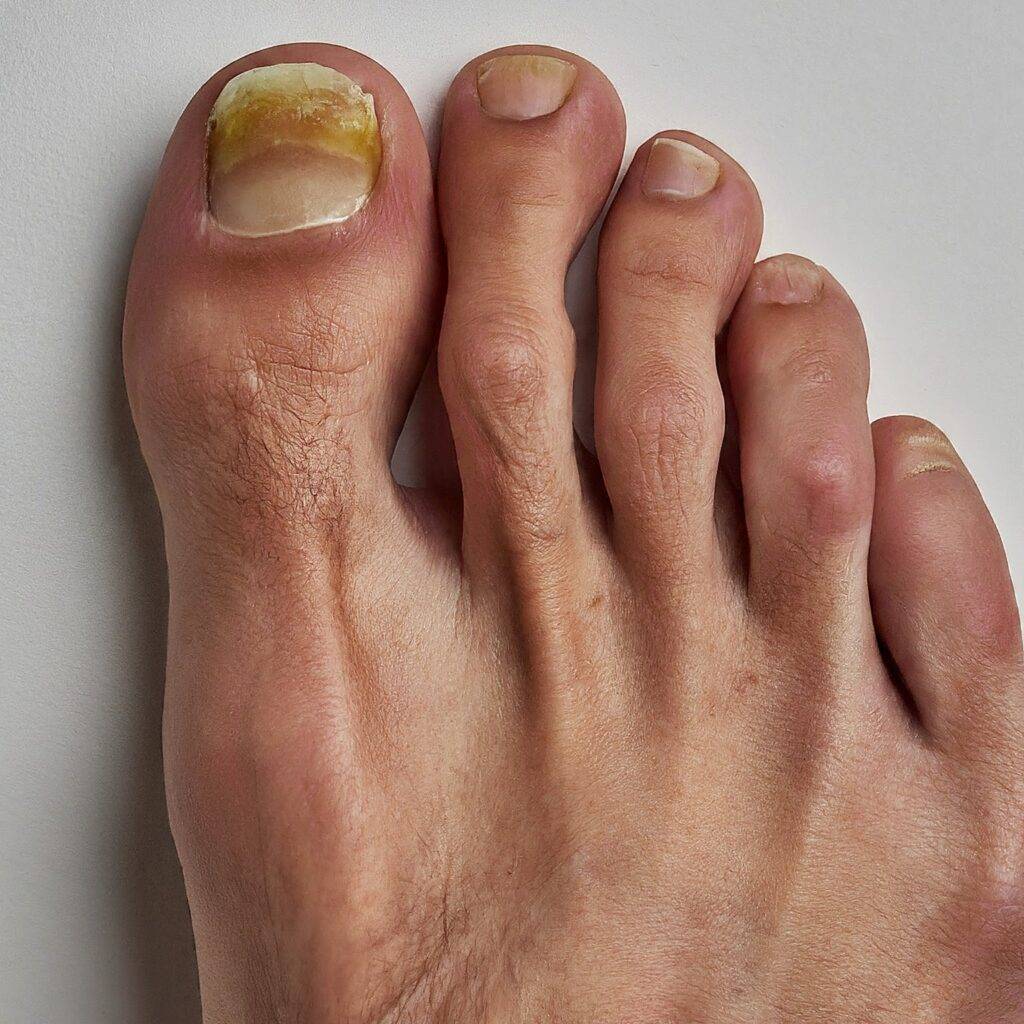
Early Stage Toenail Fungus: Don’t Ignore the Warning Signs
Stay vigilant for early signs of toenail fungus like discoloration and catch this infection in its treatable phase. Get tips to identify early stage toenail fungus and act swiftly.
Key Takeaways: Early Stage Toenail Fungus
| What is it? | Early-stage toenail fungus is a fungal infection that starts as a yellow or white discoloration affecting part of the toenail. |
| Causes | Exposure to warm, moist environments like showers, pools, or sweaty shoes can allow the fungus to take hold. |
| Signs to Watch | Discoloration, brittleness, crumbling, thickening, or distortion of the nail. |
| Treatment | Over-the-counter, topicals or oral antifungals from a doctor may help, but catching it early is crucial. |
| Prevention | Keep nails trimmed and clean, wear moisture-wicking socks, use antifungal powder, and avoid going barefoot in public areas. |
Early stage toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, can start out looking like a small, harmless discoloration but can progress into a stubborn and disfiguring nail infection if left untreated. Staying vigilant about the early signs of toenail fungus and taking prompt action is key to stopping this condition before it becomes an unsightly and potentially painful issue.
What Exactly is Early Stage Toenail Fungus?
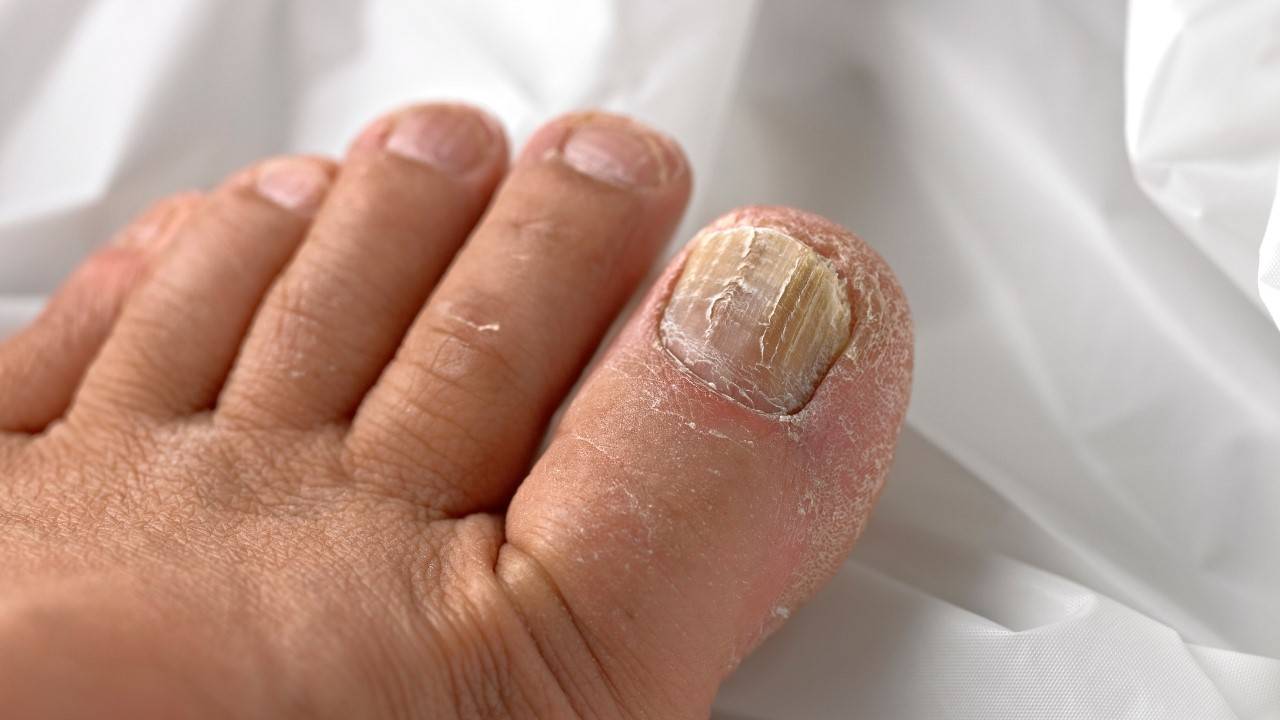
Early stage toenail fungus refers to the initial phase of a fungal nail infection when it is easier to treat and eliminate. The fungus that causes onychomycosis, usually a type of dermatophyte fungus, starts to grow in the space underneath the hard nail surface.
As the fungus spreads, it leads to the nail becoming:
- Discolored with yellow, brown, or white streaks or spots.
- Thickened and distorted in shape.
- Brittle, crumbly, and prone to breaking apart.
In the early stage, fungal infection is generally contained in a small area of one or two nails with mild discoloration and texture changes. Catching it at this point provides the best chance of successfully treating the toenail fungus before it progresses and spreads.
What Causes Early Stage Toenail Fungus?
Fungal nail infections can develop due to a few different factors:
- Warm, moist environments: Fungi thrive in warm, damp areas like showers, locker rooms, swimming pools, and sweaty shoes or socks. These places allow the fungus to remain on the feet and start burrowing under the nails.
- Nail trauma: Any damage to the nail through activities like pedicures, improper nail trimming, or injuries creates an entry point for fungus.
- Weakened Immune System: Having a suppressed immune system due to certain medications or health conditions like diabetes allows fungal infections to take hold more easily.
- Age: As you get older, your nails naturally become drier and brittle making fungal nail infection a bigger risk.
Certain people are more prone to developing toenail fungus like older adults, athletes who use public showers, people with diseases impacting circulation like diabetes, and those with general nail disorders or trauma. However, anyone can potentially develop it if exposed to the right environment where fungus proliferates.
Signs and Symptoms of Early Stage Toenail Fungus
Knowing what to look for is crucial to catching a toenail fungal infection in its earliest, most treatable phase. Early warning signs of toenail fungus to watch for include:
Discoloration
One of the most common first signs is the nail developing white or yellow streaks or spots as the fungus grows underneath and disrupts the nail surface. As the infection progresses, the discoloration can spread and the nail may turn darker yellow, brown, or even blackish.
Texture Changes
As early stage toenail fungus takes hold, the nail may start becoming thicker, more brittle, and crumbly instead of smooth. You may notice the texture becoming uneven or distorted as the nail surface becomes irregular.
Foul Smell
Some types of toenail fungus can eventually cause a foul odor as the infection worsens and the damaged nail provides an ideal environment for bacteria. An unexplained bad smell around the toes could indicate a fungal issue starting.
Pain or Discomfort
While early stage toenail fungus often starts painless, it can eventually lead to discomfort as the nail continues to thicken and crumble. Pressure, burning, or tenderness may develop, especially when wearing shoes.
Nail Distortion
As the fungus spreads further, the entire nail may become misshapen, thickened, curved, or raised off the nail bed, creating an unsightly and potentially painful deformity.
If you notice any of these changes impacting one or more toenails, it’s important to start treatment right away before the fungus continues spreading and becomes even harder to eliminate.
Risk Factors for Developing Toenail Fungus
While toenail fungus can impact anyone, certain risk factors increase your likelihood of developing this condition:
- Older Age: Risk rises as you get older due to reduced nail growth, poorer circulation, and higher potential for nail injuries.
- Nail Trauma: Any cracks, cuts, or lifts in the nail provide an entry point for fungus.
- Moist Environments: Walking barefoot in locker rooms, pools, or other damp public areas.
- Sweaty Footwear: Not changing sweaty socks and keeping feet in closed-toe, moisture-trapping shoes.
- Weakened Immune System: Diabetes, HIV/AIDS, cancer treatments, or autoimmune disorders.
- Genetics: Family history and certain genetic factors may increase risk.
- Skin Conditions: Issues like psoriasis or athlete’s foot allow the fungus to spread to nails more easily.
- Poor Foot Hygiene: Not washing and fully drying feet regularly creates a welcome environment for fungal growth.
This study found that toenail fungal infections are more common in older males with concurrent tinea pedis (athlete’s foot fungus) and peripheral vascular disease or diabetes.
Following good foot hygiene, avoiding going barefoot around public pools/showers, and addressing any underlying health conditions can help reduce your risks.
Tips to Identify Early-Stage Toenail Fungus
Catching toenail fungus in its earliest stage provides the best chance of effectively treating the infection before it becomes an entrenched, difficult problem. But how can you tell early stage toenail fungus apart from other potential nail issues?
Here are some key tips to help identify signs of fungus sooner rather than later:
Look for Discoloration Patterns
One of the hallmarks of early stage toenail fungus is discoloration that starts as singular streaks, lines, or spots rather than overall uniform staining of the whole nail. White, yellow, brown, or darkening spots beginning at the nail’s edge or sides may signal fungal growth underneath.
Consider the Location
Toenail fungus most commonly impacts the larger toenails like the big toe and progressively spreads from there to the other toes. A case of toenail fungus usually affects multiple adjacent nails rather than random, disconnected ones.
Note the Nail Texture
Beyond just discoloration, early toenail fungus can lead to noticeable textural changes making the surface uneven or crumbly. A roughened, rippling nail is another red flag versus just yellowish staining.
Rule Out Other Issues
Some nail discoloration could stem from other causes, so rule those out first:
- Dark streaks or spots may indicate an injury that caused nail staining rather than a fungus.
- Green or black discoloration could be a bacterial or psoriatic nail infection instead.
- Red, inflamed skin around nails may point to an ingrown nail rather than a fungus.
Pay Attention to the Speed of Changes
Toenail fungus usually progresses gradually over weeks and months starting with a small area of discoloration and slowly spreading. Any sudden, rapidly worsening nail changes could indicate a different, more acute issue requiring medical attention.
If you suspect early stage toenail fungus based on the location, pattern, progression, and texture changes specific to fungal nail infections, it’s wise to start treatment as soon as possible before it becomes an entrenched issue.
Professional Diagnosis of Toenail Fungus
While you can look for the typical signs yourself, it’s still recommended to have a podiatrist or dermatologist officially diagnose whether nail fungus is the culprit. This rules out look-alike conditions and ensures you receive the proper treatment.
A foot doctor can examine characteristics like:
- Appearance and pattern of nail discoloration/deformities
- Nail sample testing to identify fungal organisms.
- Skin condition around the nails
- Your symptoms, risk factors, and case history
They may take a small nail clipping or scraping to send for lab analysis that can pinpoint the specific strain of fungus. This allows them to determine the most effective medication for treatment.
In some cases, your doctor may also order blood tests to check for any underlying health issues like diabetes, circulation problems, or immune deficiencies that could be contributing factors.
Treatment for Early Stage Toenail Fungus
The earlier you start treating toenail fungus, the higher your chances of eliminating it before it becomes an entrenched, difficult-to-treat problem. For early stage cases, your doctor will likely first recommend one or more of these therapies:
Topical Treatments
These include nail lacquers, solutions, or polishes that get brushed directly onto the infected nails to help stop fungal growth. Common ingredients like ciclopirox or amorolfine gradually get absorbed through the nail to attack fungus underneath.
Oral Antifungal Medications
Pills like terbinafine or itraconazole are taken daily for several weeks or months to send antifungal medication through your bloodstream to the infected nails. These may be prescribed for more widespread or severe cases of toenail fungus.
Removal of Infected Nail
In limited cases where the infection seems contained to just one small area, your doctor may remove or trim away that portion of the nail to help topical treatments penetrate better. A new, hopefully, clear nail can then regrow over time.
Laser or Photodynamic Therapy
These methods use specific light wavelengths to directly target and kill fungus through the nail without oral medications. Multiple treatments are usually required.
The sooner you start treating early toenail fungus when it’s easiest to reach with medications, the better your outcome. If caught early, you may only need an 8 to 12-week course of topical treatment to completely clear the infection.
But the longer you delay treating it, the more entrenched the fungus becomes and the harder it is to eliminate even with oral medications or removal of the infected part of the nail.
So don’t wait if you suspect those initial warning signs of early stage toenail fungus! Make an appointment with a podiatrist or dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and get started on treatment right away.
Home Care & Prevention Tips for Toenail Fungus
While professional treatment provides the most effective way to overcome toenail fungus, you can take some proactive steps at home to control its spread and prevent future infections:
Keep Feet Dry & Nails Trimmed
- Regularly trim toenails straight across to reduce trauma and areas for fungus to grow
- Ensure feet stay clean and completely dry, especially between toes after bathing
- Use an antifungal powder on your feet and inside shoes to kill fungal spores.
Choose Breathable Footwear
- Wear moisture-wicking socks that prevent sweating and dampness around the toes
- Go barefoot in shoes/sandals, when possible, to increase air exposure and drying.
- Alternate between different shoes day-to-day to allow drying time.
Disinfect Thoroughly
- Use UV shoe sanitizer or antifungal spray on footwear.
- Discard old shoes and socks harbouring fungus.
- Fully clean and dry bathing areas, floors, and towels regularly
Avoid Nail Injuries or Fungal Exposure
- Never go barefoot in public pools, showers, or locker rooms
- Use a foot grooming tool for safe nail trimming instead of scissors.
- Don’t get pedicures at facilities that don’t properly sterilize tools.
Maintain Good General Health
- Control any conditions like diabetes that increase fungal infection risks.
- Eat a nutritious diet and stay active to boost your immune defences.
- Stop nail-biting habits that damage nails and create entry points.
See a Podiatrist Annually
- Routine foot exams allow a doctor to monitor nail health.
- They can catch any early fungal growth before it spreads.
- Ongoing treatment adjustments can be made as needed.
By following good preventive foot care, you reduce future risks even after clearing up an initial bout of toenail fungus. Staying vigilant and acting quickly at the first signs provides the best chance of stopping fungal nail infections before they take over.
When to See a Doctor for Toenail Fungus
If you notice any of the following signs and symptoms, it’s recommended to make an appointment with a podiatrist or dermatologist:
- Discolored, thickened, brittle, or misshapen toenails.
- White or yellow streaks develop on the nails.
- Darkening nails, especially if they spread rapidly.
- Crumbly, chalky debris coming off the toenails.
- Foul odor coming from the toenails.
- Discomfort, pain, or temperature sensitivity in the toenails.
- Toenail fungus that doesn’t improve with home treatment after several months.
A doctor can examine the nails closely, take a sample to confirm if the fungus is the underlying cause, and determine if oral or prescription-strength medications are needed based on the severity and extent of the infection.
While toenail fungus may not be a medical emergency, it’s still important not to ignore it and let it spread further. Delaying treatment makes it harder to fully eliminate the infection and clear those unsightly, damaged nails. See a foot specialist promptly if you suspect toenail fungus, especially in its early phase when it’s most treatable.
When Should You Worry About Toenail Fungus Complications?
In otherwise healthy people, toenail fungus may just be an unsightly inconvenience. But in some cases, it can potentially lead to larger issues that need prompt medical care:
Severe Pain or Infection If your toenail fungus causes extreme, worsening pain; redness and swelling of the toe; fever; or pus/discharge, it could indicate a more serious secondary bacterial skin infection that requires antibiotic treatment.
Nail Loss With very advanced, untreated toenail fungus, the entire toenail may become too deteriorated and loosen, leading to permanent nail loss. See a doctor if you lose more than just small, crumbled pieces.
Nail Abnormalities or Growths While extremely rare, some strains of toenail fungus have been linked to the development of abnormal nail growths leading to nail tumours. Have any suspicious nail lesions or masses evaluated.
Spread to Other Areas If the fungus spreads beyond the nails to the surrounding skin, it could be a more invasive fungal infection requiring oral medications.
Complications from Diabetes/Poor Circulation In people with diabetes, poor circulation, or compromised immune systems, any infection including toenail fungus poses heightened risks. It could worsen and spread to deeper tissues/bones, become harder to treat, and lead to complications like diabetic foot ulcers.
If you have an underlying condition or the toenail fungus seems severe, painful, rapidly worsening, or not responding well to treatment, don’t hesitate to follow up with your doctor. Otherwise, healthy people can usually treat a case of early stage toenail fungus conservatively, but any concerning changes warrant professional medical evaluation.
Conclusion
early stage toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a fungal infection that begins as a yellow or white discoloration affecting part of the toenail. Key takeaways from this discussion include the importance of recognizing signs such as discoloration, brittleness, or thickening of the nail; understanding common causes like warm, moist environments, nail trauma, and weakened immune systems; considering treatment options such as over-the-counter topicals or oral antifungals from a doctor, with early detection being vital; and implementing preventive measures like keeping nails trimmed and clean, wearing moisture-wicking socks, and avoiding barefoot exposure in public areas to reduce the risk of infection. Early intervention is crucial to prevent the condition from worsening and becoming more challenging to treat. By understanding the early signs and taking proactive steps, individuals can effectively manage and prevent the spread of toenail fungus.

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.