Avoid Cardiac Arrest: Simple Lifestyle Changes
Prevent Cardiac Arrest It is a medical emergency that can happen when the heart stops beating all of a sudden.
The American Heart Association says that more than 350,000 heart attacks happen outside of hospitals in the United States every year. Understanding how to prevent this life-threatening illness is crucial.
This post will explore modest lifestyle adjustments that could avoid cardiac arrest.
From quitting smoking to stress management, we’ll discuss ways to protect your heart and lower your chance of it.
So let’s discover how to manage your heart’s health.
Risk Factors

It is a serious medical condition that can have many causes.
The following list includes some of the most common risk factors for cardiac arrest:
Frequent Risk Factors
Age: As we age, our risk of developing cardiac arrest increases. This is because the heart muscle can become weaker over time, making it more difficult for the heart to pump blood effectively.
Gender: Men are at a higher risk of cardiac arrest than women. Men are more likely to have preexisting conditions like high blood pressure or high cholesterol, both of which can contribute to cardiac arrests. Women, on the other hand, are less likely to have these illnesses.
Family history: If a close family member, like a parent or sibling, has had a cardiac arrest, your chance of getting one is higher.
Existing health conditions: Certain health conditions Coronary artery disease, heart failure, and other heart rhythm disorders increase your risk of cardiac arrest.
Lifestyle factors that increase the risk
Smoking: Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for cardiac arrest.
It can damage the blood vessels and lead to the buildup of plaque, which might lead to a heart attack or even death. Poor diet: saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars raise the risk of heart disease, which can lead to cardiac arrest. Lack of exercise: Regular exercise can help improve cardiovascular health and lower the risk of getting heart disease, which is a major risk factor for it.
Stress: Stress that lasts for a long time can make you more likely to get heart disease and could even lead to a heart attack. By understanding the common risk factors for it, you can take steps to reduce your risk and stay healthy. The next section will focus on the lifestyle changes you can make to prevent it.
Preventing Cardiac Arrest Through Lifestyle Changes

You can greatly lower your chances of getting heart disease and experiencing cardiac arrest by making a few straightforward adjustments to the way you live your life.
Go to a medical professional as soon as possible if you have any questions or concerns regarding the state of your heart.
Here are some tips on how to prevent heart attack :
Quit smoking
Smoking is one of the main reasons why people get heart disease and have a cardiac arrest.
When you stop smoking, your chances of getting heart disease go down, and your health as a whole gets better.
Benefits of quitting smoking:
reduced risk of heart disease
Improved lung function
Lower blood pressure
Better circulation
reduced risk of stroke and cancer
Strategies to quit smoking:
Nicotine replacement therapy (such as patches or gum)
Medications prescribed by a healthcare provider
Counselling or support groups
Avoiding triggers and changing routines
Staying active to reduce cravings
Adopt a healthy diet
Eating a healthy, well-balanced diet is the most important thing you can do to keep your heart healthy and avoid cardiac arrest. A diet that is good for your heart should include a variety of foods that are high in nutrients and low in foods that are high in saturated fat, salt, and added sugars.
Foods to include in a heart-healthy diet:
Fruits and vegetables
Whole grains
Lean proteins (such as fish, poultry, and beans)
Low-fat dairy products
Nuts and seeds
Healthy fats (such as olive oil and avocado)
Foods to avoid:
Processed foods high in saturated fat, salt, and added sugars
Red meat and processed meats (such as bacon and sausage)
Sugary drinks (such as soda and sports drinks)
Foods high in cholesterol (such as egg yolks and organ meats)
Engage in regular exercise.
Physical activity must be done regularly to keep the heart healthy and lower the risk of cardiac arrest. Physical activity has been shown to reduce stress, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
Benefits of exercise:
Lower blood pressure
Improved cholesterol levels
Reduced stress
increased stamina and endurance
reduced risk of obesity and diabetes
Types of exercise to consider:
Aerobic exercise (such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming)
Work on your muscles (such as with weightlifting or resistance bands).
Yoga or stretching
Sports or recreational activities
Manage stress
Stress that lasts for a long time can make heart disease worse and make cardiac arrest more likely. Learning how to manage stress can help reduce the risk and improve overall health.
Techniques to manage stress:
Deep breathing exercises
Meditation or mindfulness practices
Yoga or Tai Chi
Spending time in nature
Listening to music or engaging in hobbies
Seeking professional help if needed
The importance of relaxation:
Relaxing is an important part of dealing with stress and can help lower the risk of a heart attack.
It has been shown that having a regular relaxation routine is good for your heart health because it lowers blood pressure, inflammation, and stress.
Getting into a state of relaxation can be helped by techniques like progressive muscle relaxation, visualizing, and guided imagery.
By making these simple changes to your lifestyle, you can greatly lower your chances of getting heart disease or having cardiac arrest. If you have any concerns about your heart’s health, be sure to speak with a healthcare provider.
Other Ways to Protect Your Heart Health

While lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk of cardiac arrest, there are other ways to protect your heart’s health as well.
Get regular check-ups with a healthcare provider.
Regular checkups with a doctor or nurse can help find and treat things that put you at risk for cardiac arrest.
During a check-up, your healthcare provider may check your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other vital signs, as well as discuss any symptoms or concerns you may have.
If you have these risk factors, you should get regular checkups. Your doctor can help you develop a plan to control risk factors and monitor heart health.
Take your medication as prescribed
If you already have health problems like high blood pressure or diabetes, taking medication as prescribed can help manage these conditions and reduce your risk of cardiac arrest. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for taking medication, including the dosage, frequency, and timing.
The importance of medication adherence cannot be overstated. Skipping doses or stopping the medication abruptly can have serious consequences for your health. If you have difficulty remembering to take medication, consider using a pillbox, setting reminders on your phone, or enlisting the help of a family member or caregiver.
Manage other health conditions
Other health problems, like sleep apnea or problems with your thyroid, can also make you more likely to have a heart attack. It’s important to take care of these conditions by getting regular checkups, managing your medications, and making changes to your lifestyle, as your doctor tells you to do.
In addition, if you have a family history of cardiac arrest or other heart conditions, it’s important to discuss this with your healthcare provider. They may recommend additional screenings or tests to assess your risk.
Learn CPR and how to use an AED.
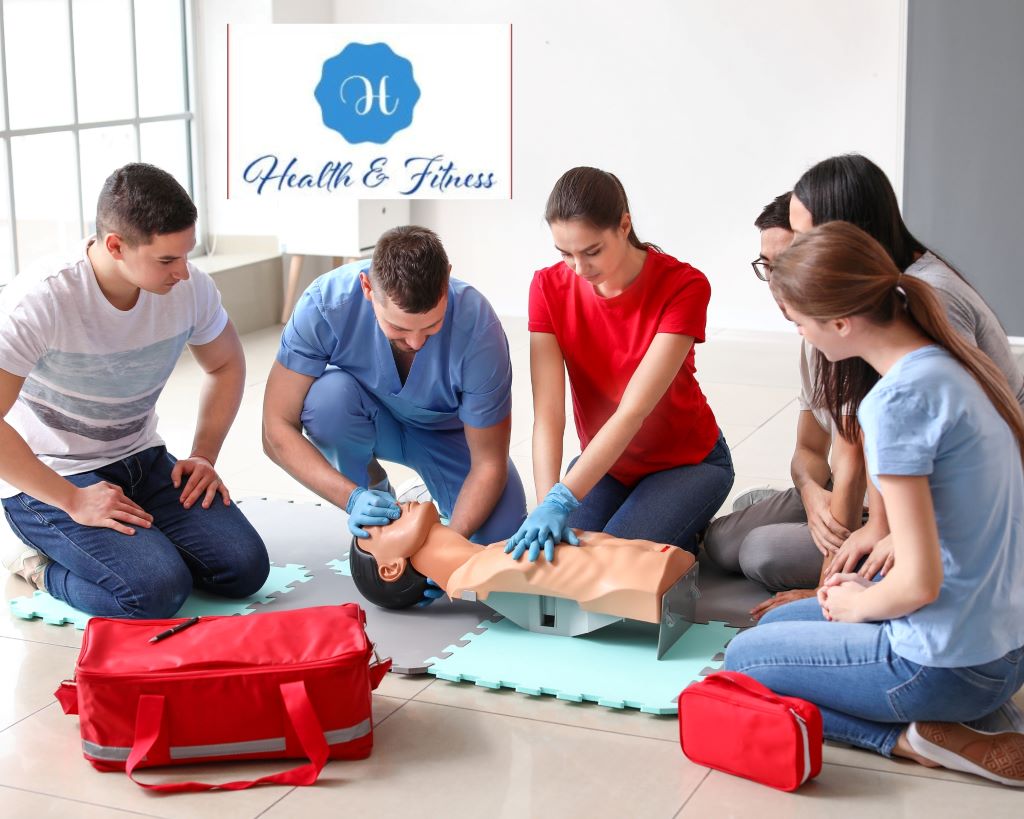

Cardiac arrest can happen suddenly and without warning, and when it comes to treatment, every minute counts. Learning CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) and how to use an AED (automated external defibrillator) can help save a life in the event of a cardiac emergency.
Many organizations offer CPR and AED training, like the American Heart Association and the American Red Cross.
By learning these life-saving skills, you can play an important role in protecting the heart health of yourself and those around you.
Overall, avoiding cardiac arrest requires several steps, such as making changes to your lifestyle, getting regular checkups, managing your medications, and taking other steps to protect your heart health.
You can lower your risk of heart attack and live a healthier, happier life by taking steps to manage your risk factors and put your heart health first.
Conclusion
Preventing cardiac arrest is critical for maintaining heart health and avoiding potentially fatal consequences.
By making simple changes to your lifestyle, like quitting smoking, eating healthier, getting regular exercise, dealing with stress, getting regular checkups, and taking your medicine as prescribed, you can cut your risk of heart attack by a lot.
Remember, small changes can make a big difference in protecting your heart health.