Best 10 Treatments and Therapies for Hepatitis B
Discover the top 10 treatments and therapies for Hepatitis B. Learn about antiviral medications, interferon injections, liver transplants, and more
Untreated hepatitis B can cause severe health problems. In 2019, the WHO projected that 257 million people had chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatitis B causes fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice and is shared through blood or bodily fluids. Hepatitis B has no cure, but many treatments can manage the virus and lesson complications.
For the most excellent care, hepatitis B patients must stay up with therapy and diagnostic breakthroughs.
This blog post discusses. It’s standard treatments, emerging therapies, and diagnostic advances.
We will also address lifestyle changes and the importance of medical advice for Hepatitis B management.

Advancements in Hepatitis B Diagnostics
Early and accurate detection is crucial for effectively treating and managing Hepatitis B.
The diagnosis of Hepatitis B has undergone significant changes over the years, highlighting the advancements made in medical technology and research.
New and better tests have become available.
Here are the Best ten treatments and therapies for Hepatitis B:
- HBV DNA Testing
HBV DNA testing is a sensitive and specific test that detects the presence of the Hepatitis B virus in the blood. This test is beneficial for monitoring the disease’s progress and the effectiveness of treatment.
Recent advancements in HBV DNA testing have improved its accuracy and speed, making it an indispensable tool in diagnosing and managing Hepatitis B.
- Serological Markers
Serological markers are proteins or antibodies that the immune system produces in response to Hepatitis B infection. These markers can be detected in the blood and used to diagnose and monitor the progress of the disease.
Recent advancements in serological markers have improved their sensitivity and specificity, allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnosis of Hepatitis B.

- Point-of-Care Testing
Diagnostic tests that can be conducted outside of a conventional laboratory environment, like at a doctor’s office or in the field, are known as point-of-care testing.
These tests are rapid and can provide results within minutes, allowing for quicker diagnosis and treatment of Hepatitis B. Several point-of-care tests for Hepatitis B are currently being developed and undergoing clinical trials.
- Non-invasive Testing
Non-invasive testing refers to diagnostic tests that do not require a blood sample or invasive procedure. These tests can include imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans, as well as histography, a technique that measures liver stiffness as an indicator of liver damage.
Non-invasive testing is beneficial for monitoring the progression of Hepatitis B-related liver disease, as it can provide valuable information with no need for a biopsy. These Hepatitis B diagnostic advances have enhanced disease diagnosis and management, improving patient outcomes.
We can expect more advanced and accurate diagnostic tests as the study proceeds.
Current Standard Treatments for Hepatitis B
Long-term hepatitis B may cause liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, and malignancy.
Hepatitis B can’t be cured, although various treatments help manage it. Antivirals, interferon, and liver transplantation cure hepatitis B.
Treatment depends on infection severity, liver damage, age, health, etc.
- Antiviral Medications
Long-term Hepatitis B is usually treated with antivirals.
These drugs block the virus from multiplying, avoiding liver damage.
Notcher, tenofovir, and lamivudine treat Hepatitis B.
Antivirals must be used long-term, perhaps forever, to prevent the virus from returning. These medications may interact with others and cause headaches, nausea, and diarrhea. Regular liver function and viral load monitoring ensure drug efficacy.
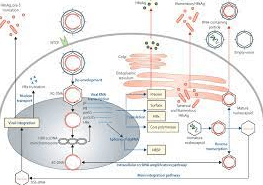
- Interferon Injections
Interferon injections cure Hepatitis B.
These injections strengthen the body’s immunological response to the virus, reducing the illness.
Interferon injections may produce flu-like symptoms, depression, and autoimmune diseases. Hence, they are reserved for milder Hepatitis B infections. Interferon injections last 6–12 months. Evaluation of therapy efficacy requires liver function and viral load monitoring.
Advanced liver disease or other medical problems may exclude interferon injections.
- Liver Transplant
Hepatitis B may destroy the liver, requiring a liver transplant.
A donor liver replaces a sick liver.
This life-saving operation is risky and short on donors’ livers.
Individuals with end-stage liver disease or liver cancer may have a liver transplant when alternative therapies fail. The liver must be monitored after transplantation to prevent rejection and other complications. Some people may utilize these essential Hepatitis B therapies to prevent problems. Long-term antiviral medications and interferon injections are more intrusive.
Researchers seek improved Hepatitis B therapies.
Best 10 Treatments and Therapies for Hepatitis B
Emerging Therapies for Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is now treated with antiviral drugs, interferon injections, and liver transplants. Researchers are investigating novel treatments to enhance patient results.
Here are some of the emerging therapies for Hepatitis B:
- RNA Interference Therapy
Hepatitis B treatment with RNA interference is promising.
Small RNA molecules suppress virus-replicating genes in this treatment.
This prevents viral spread and liver damage.
Initial clinical studies of RNA interference therapy reveal outcomes, demonstrating its potential.
- Therapeutic Vaccines
Hepatitis B therapeutic vaccines are also being developed. These vaccinations boost the immune system to fight the infection. Therapeutic vaccinations cure diseases rather than prevent them. Several Hepatitis B therapeutic vaccines are being tested.
- Combination Therapies
Besides exploring RNA interference therapy, researchers are also investigating combination therapies to improve outcomes for Hepatitis B patients. For instance, combining antiviral medications with interferon injections or using different antiviral medications together has shown potential to enhance treatment effectiveness and minimize the risk of drug resistance. Such therapies are currently being tested in clinical trials, and early results are promising.
- Gene Editing
Gene editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 are also being studied as a potential therapy for Hepatitis B. A molecular scissors-like tool removes virus DNA from host cells, curing the patient. Hepatitis B may be cured by gene editing, which is still in research. These experimental Hepatitis B treatments give hope for better treatment.
Before adopting a new therapy, weighing the pros and cons and assessing its safety and success is essential.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Managing Hepatitis B
Untreated hepatitis B may be dangerous.
Lifestyle changes may assist antiviral medications in treating hepatitis B.
People living with Hepatitis B may remain healthy with lifestyle changes.
- Maintain a healthy diet.
People living with Hepatitis B, especially, require a balanced diet.
Vegetables, fruits, grains, and lean protein improve liver function and reduce issues.
Avoid alcohol and processed foods, which damage the liver.
- Exercise regularly
Exercise improves liver function, reduces inflammation, and improves wellness.
Brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for 30 minutes most days is ideal.
- Get enough rest
Getting enough rest is essential for liver health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and establish a regular sleep schedule. If you have trouble sleeping, try relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation,
or yoga.
- Avoid risky behaviors
Sharing needles and unprotected contact promotes Hepatitis B.
If unsure, have Hepatitis B. Diagnose and treat early.
- Manage stress
Stress reduction helps the liver. Deep breathing, family, meditation, and exercise assist.
Diet and antivirals might treat hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B patients may improve liver function by eating, exercising, relaxing, avoiding dangerous behaviors, and regulating stress.

Conclusion
Hepatitis B may cause liver disease and cancer. Better diagnosis and treatment are needed. RNA interference and therapeutic vaccines may assist Hepatitis B patients. HBV DNA testing is non-invasive.
Early detection and treatment may prevent hepatitis B.
Therefore, persons at risk of Hepatitis B should be tested and vaccinated.
Despite our poor knowledge of Hepatitis B, new treatments, and diagnostics promise to improve patient outcomes.
Research may cure Hepatitis B.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Hepatitis B: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/index.htm
- Hepatitis B Foundation: https://www.hepb.org/

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.


