14 Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency: Shedding Light on Your Health Warning Signs
Discover the 14 signs of Vitamin D deficiency, crucial health warning signs. Shedding light on your well-being – don’t miss these vital insights.
Introduction to 14 Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency

Uncover 14 signs of vitamin D deficiency and their impact on your health. Recognize these warning signals and avoid vitamin D insufficiency. Shed light on your well-being with insights into the signs, symptoms, and solutions for 14 signs of vitamin D deficiency. Are you feeling tired, achy, or simply not at your best? It may indicate vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D, the “sunshine vitamin,” is essential to health. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the 14 telltale signs of vitamin D deficiency, its causes, the importance of vitamin D for your body, and practical steps to address this common deficiency.
Understanding what is the Vitamin D Deficiency
A vitamin D deficit develops when the body does not get enough of this crucial nutrient. Consequently, this deficiency can impair optimal bodily function, giving rise to various symptoms and potential health issues.
14 Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
Let’s delve into the 14 signs that may indicate a vitamin D deficiency:
1. Fatigue and Lack of Energy
Feeling constantly tired, even after a night’s sleep? Vitamin D deficiency can contribute to persistent fatigue and a general lack of energy.
2. Frequent Illnesses and Weakened Immune System
If you catch colds, flu, or other infections more frequently, it could indicate compromised immune function resulting from vitamin D deficiency. Inadequate vitamin D levels may leave your immune system vulnerable, making you more susceptible to frequent illnesses and infections.
3. Bone and Joint Pain
Vitamin D is essential for maintaining healthy bones and joints. Deficiency can lead to bone and joint pain, along with an increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
4. Muscle Weakness and Aches
Experiencing muscle weakness, aches, or difficulty performing physical tasks? Inadequate vitamin D levels may contribute to these discomforts.
5. Depression and Mood Swings
Studies have linked vitamin D insufficiency to mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. If you’re feeling down or experiencing mood swings, it’s worth considering the role of your vitamin D levels.
6. Hair Loss and Thinning
While hair loss can have multiple causes, low vitamin D levels may contribute to hair loss and thinning in some individuals.
7. Slowed Healing of Wounds
Vitamin D insufficiency may be linked to impaired immunological function, leading to slow wound healing.
8. Bone Loss and Increased Fracture Risk
Vitamin D is crucial for bone health, and deficiency can result in reduced bone density and an increased risk of fractures.
9. Impaired Cognitive Function
Some studies suggest a connection between vitamin D deficiency and cognitive decline, including memory problems and difficulty thinking clearly.
10. High Blood Pressure
Achieving and keeping a healthy vitamin D level may aid in maintaining normal blood pressure. Deficiency, on the other hand, may contribute to hypertension.
11. Dental Issues
An increased risk of dental problems, such as gum disease and tooth decay, has been associated with vitamin D deficiency.
12. Sleep Disturbances
Struggling with sleep disturbances or insomnia? Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to disruptions in sleep patterns.
13. Reduced Endurance and Stamina
Inadequate vitamin D levels may affect physical performance, reducing endurance and stamina during activities.
14. Digestive Issues
Some individuals with vitamin D deficiency may experience digestive issues like abdominal pain, constipation, or diarrhea.
What Causes Vitamin D Deficiency?
Several factors can contribute to vitamin D deficiency:
- Lack of Sun Exposure: Sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D. Limited sun exposure, especially in regions with less sunshine, can lead to poverty.
- Darker Skin Pigmentation: People with darker skin naturally have higher melanin levels, which can reduce vitamin D synthesis in the skin.
- Age: As you age, your skin produces less vitamin D, leaving older persons more susceptible to shortage.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can interfere with vitamin D absorption and utilization, increasing the risk of deficiency.
- Limited Dietary Intake: Vitamin D is found in a few food sources, and those with restricted diets or specific dietary preferences may struggle to get enough from food alone.
The Importance of Vitamin D for Your Health
Vitamin D is essential for numerous bodily functions and supports overall health and well-being. Here are some critical roles that vitamin D plays in your body:
1. Bone Health
Bone health and strength depend on calcium; vitamin D helps the body absorb the mineral. It helps prevent bone loss, fractures, and conditions like osteoporosis.
2. Immune Function
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating immune function, helping to defend against infections, autoimmune disorders, and other immune-related conditions.
3. Mood and Mental Health
Adequate vitamin D levels are associated with improved mood, reduced risk of depression, and enhanced cognitive function.
4. Muscle Function
Vitamin D is necessary for proper muscle function and strength. It supports muscle contraction and helps reduce the risk of muscle weakness and pain.
5. Heart Health
Maintaining optimal vitamin D levels may support cardiovascular health, lowering the danger of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and excessive blood pressure.
6. Cancer Prevention
Research shows vitamin D may prevent colon, breast, and prostate cancer.
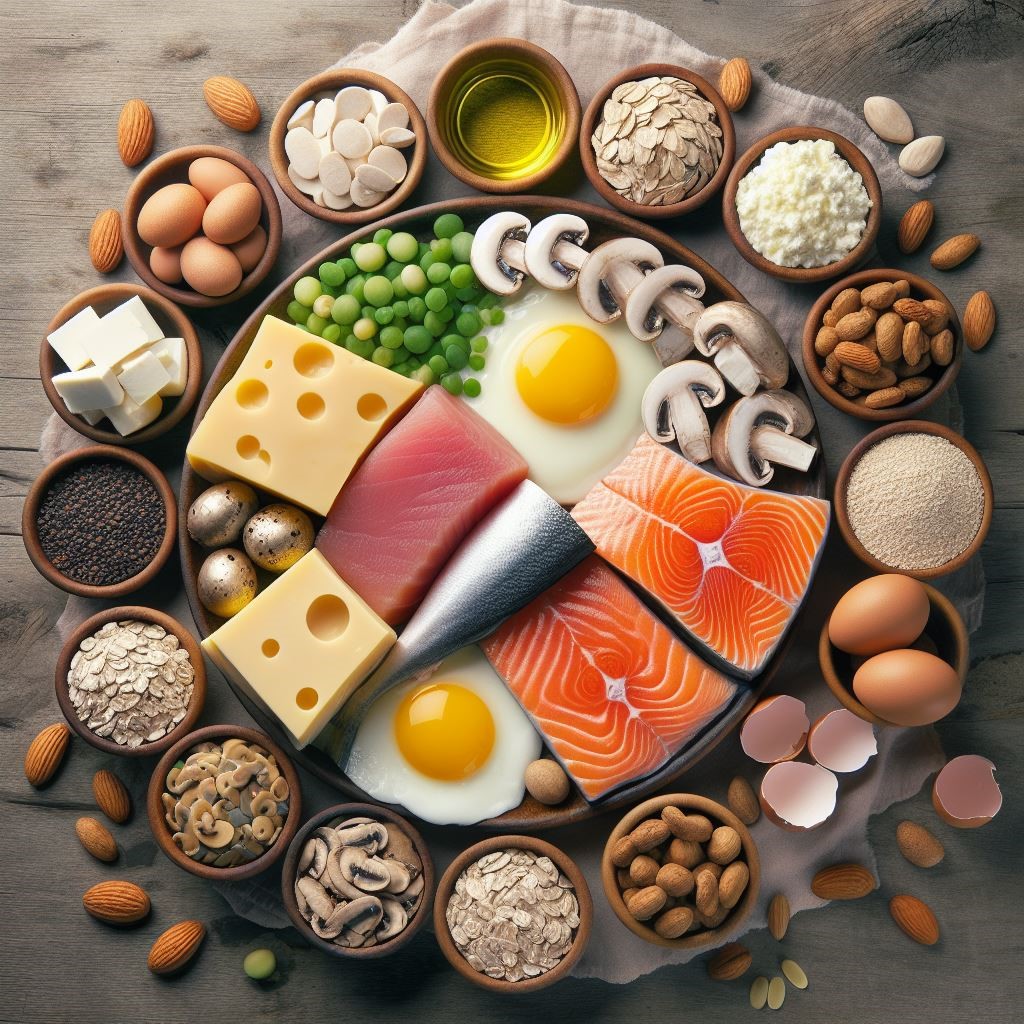
Foods Rich in Vitamin D
Boosting your vitamin D levels can be achieved by incorporating specific foods into your diet. Here are some top sources of vitamin D:
- Fatty Fish: salmon, mackerel, and trout are excellent choices.
- Fortified Dairy Products: milk, yogurt, and cheese fortified with vitamin D.
- Egg Yolks: A natural source of vitamin D.
- Mushrooms: Some varieties, especially when exposed to sunlight, contain vitamin D.
- Cod Liver Oil: A concentrated source of vitamin D.
- Fortified Cereals and Plant-Based Milk Alternatives: Check for vitamin D fortification.
- Beef Liver: Contains vitamin D, but consumed in moderation.
- Cheese: Swiss and cheddar varieties offer small amounts of vitamin D.
- Tofu: A plant-based source of vitamin D.
- Sun-Dried Shiitake Mushrooms: Provide vitamin D when dried under sunlight.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help support your vitamin D intake. Remember to maintain a balanced and varied diet for overall nutritional well-being.
Addressing Vitamin D Deficiency
If you suspect you have a vitamin D deficiency based on the signs discussed, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance. They may recommend a blood test to calculate your vitamin D levels.
Frequently Asked Questions About 14 Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
Q1: Does sun exposure alone provide adequate vitamin D?
While sunlight is an excellent source of vitamin D, the amount you can produce depends on factors like your location, time of year, skin tone, and sun protection practices.
Q2: How can I increase my vitamin D levels through diet?
Vitamin D may be found in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), fortified dairy products, egg yolks, and sun-exposed mushrooms. In certain circumstances, dietary supplements may be required.
Q3: Is it safe to take vitamin D supplements?
When taken as directed, vitamin D supplements are safe. However, following recommended dosages and consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance is essential.
Q4: Can I get too much vitamin D?
Excessive vitamin D intake can lead to toxicity, causing symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and kidney problems. It’s crucial to follow recommended dosages and not exceed safe limits.
Q5: How long does it take to compensate for a lack of vitamin D?
The time required to correct a vitamin D deficiency varies depending on the individual’s levels, dosage, and overall health. It may take weeks to months to reach optimal levels.
Q6: Can vitamin D deficiency be prevented?
Maintaining adequate sun exposure, consuming vitamin D-rich foods, and considering appropriate supplementation can help prevent vitamin D deficiency.
Q7: Can I get enough vitamin D from indoor tanning beds?
Indoor tanning beds are not recommended as a source of vitamin D. They pose potential health risks because of ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure.
Q8: Are there groups more at risk of vitamin D deficiency?
Certain groups, such as older adults, people with darker skin tones, those with limited sun exposure, and individuals with specific medical conditions, may have a higher risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Q9: Can vitamin D deficiency affect children?
Vitamin D deficiency can affect children, leading to issues like rickets (soft bones) and delayed growth. Adequate vitamin D is crucial for healthy development.
Q10: Can symptoms alone be used to diagnose vitamin D deficiency?
While symptoms may indicate vitamin D deficiency, accurately diagnosing the condition and determining the appropriate treatment requires a blood test.
Q11: Are there any side effects of vitamin D supplementation?
When taken as directed, vitamin D supplements are safe. However, individuals may experience minor side effects, such as nausea, constipation, or allergic responses. It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Q12: Can I take vitamin D supplements if I have certain medical conditions?
It’s essential to inform your healthcare professional about any existing medical conditions, as certain conditions may require adjustments in vitamin D supplementation.
Q13: How often should I get my vitamin D levels checked?
The frequency of vitamin D level checks depends on various factors, including your initial levels, response to supplementation, and healthcare professionals’ recommendations.
Q14: Can vitamin D deficiency be reversed?
Vitamin D deficiency can be reversed through appropriate interventions, including sun exposure, dietary changes, and supplementation under healthcare professional guidance.
Conclusion about 14 Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
In this blog post, we highlighted 14 signs of Vitamin D Deficiency.
Vitamin D deficiency can significantly affect your overall health and well-being, profoundly affecting various bodily functions. Therefore, recognizing the signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency is crucial for timely intervention and proactive measures. By seeking a proper diagnosis, addressing deficiencies through lifestyle modifications or supplementation, and regularly monitoring your vitamin D levels, you can ensure optimal health and vitality. Remember, if you want particular advice about your situation, it’s better to talk to a doctor.
Reference
Holick, M. F. (2007). Vitamin D deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine, 357(3), 266-281. Link
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium. (2011). Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. National Academies Press. Link.