Dive deeper into Emphysema vs. COPD: Uncover the nuances. Expert insights to understand the differences and manage your health effectively.
Introduction
Emphysema vs. COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) are two common respiratory conditions affecting millions worldwide. Both conditions are often discussed because they share similar symptoms and can occur together. However, they are distinct conditions with different causes and treatments.
In this blog post, we’ll go beyond the basics and explore the nuances of Emphysema vs. COPD. We’ll look at each condition, how they are related, and how they differ. Emphysema vs. COPD: Exploring the differences between these respiratory conditions is crucial for informed health decisions. We’ll delve into each condition’s symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Let’s uncover the details together.
What is Emphysema?

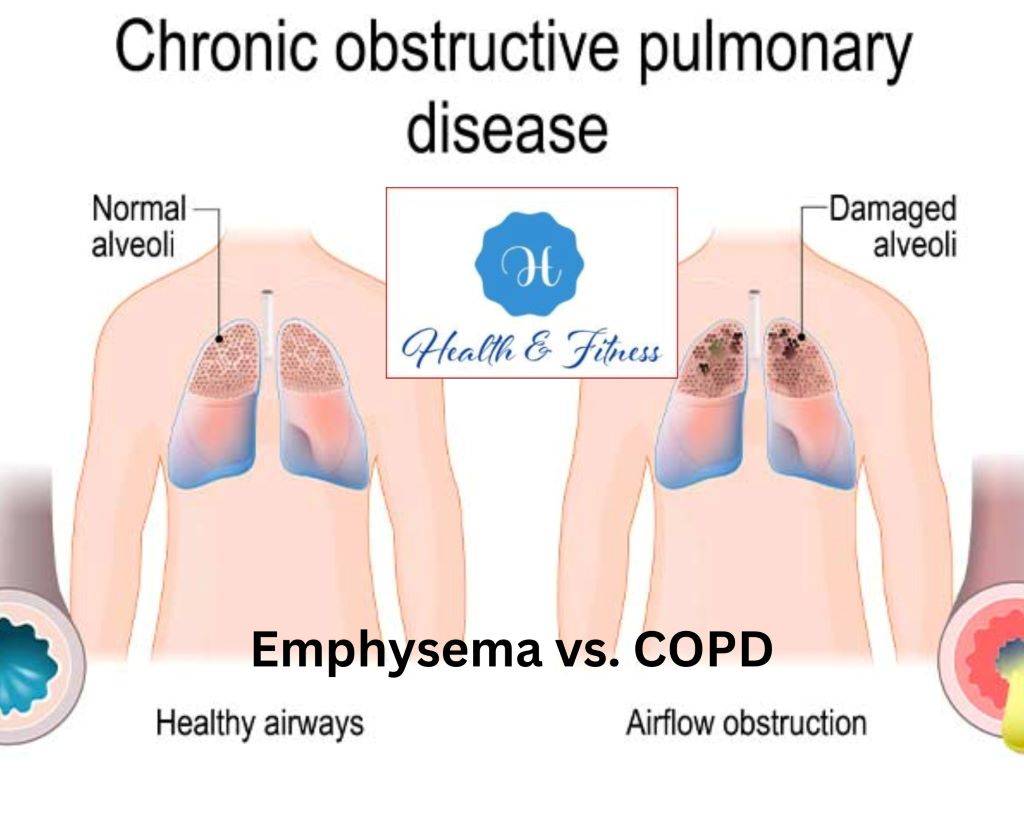
Emphysema and COPD can impact an individual’s quality of life. Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that damages the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, making breathing difficult. This damage occurs when the walls of the air sacs become weak and break down, resulting in fewer, more significant air gaps than many smaller ones.
Shortness of breath and other symptoms develop because less oxygen can enter the circulation.
What is COPD?
People with COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) have trouble breathing because of continuous inflammation and damage to their airways. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema, the two most prevalent forms of COPD, may produce similar symptoms.
The Overlap: How Emphysema and COPD Are Related(Emphysema vs. COPD)
Emphysema vs. COPD: Understanding the connection is key. Emphysema is one of the two main types of COPD. While they have similarities, COPD is a group of lung disorders causing breathing issues from airway inflammation, while emphysema specifically damages lung air sacs. People with emphysema often have COPD, and vice versa. Untreated COPD can lead to emphysema over time, as airway damage extends to the lung sacs. Differentiating between the two can be challenging, especially in the early stages.
The Differences: Understanding the Nuances of Emphysema vs. COPD
While emphysema and COPD are related, they are distinct conditions with some crucial differences. Emphysema specifically refers to the destruction of the air sacs in the lungs, while COPD is a broader term that encompasses a group of lung diseases that cause breathing difficulties.
Emphysema vs. COPD causes: Smoking, air pollution, and chemical fumes are the leading causes of emphysema.
Smoking and long-term lung irritant exposure are the leading causes of COPD.
Symptoms and Diagnosis: How to Tell the Emphysema vs. COPD
It’s hard to distinguish emphysema from COPD since they share similar symptoms. Particularly significant distinctions might aid diagnosis. Emphysema Manifestations Shortness of breath, particularly during exercise, is a classic sign of emphysema. As the condition progresses, shortness of breath may become more severe and occur with less exertion.
Chronic cough, chest tightness, wheezing, and exhaustion may ensue. COPD symptoms vary by severity, but persistent cough, shortness of breath, and sputum production are the most prevalent. Individuals with severe COPD may also experience unintended weight loss, fatigue, and frequent respiratory infections.
Diagnosis of Emphysema and COPD usually involves a combination of medical history, physical exam, and pulmonary function tests. Imaging tests such as CT scans may also be used to confirm a diagnosis of emphysema. Sometimes, a lung biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
One key difference in the diagnosis of emphysema and COPD is the use of lung function tests. Emphysema is typically diagnosed using a test called spirometry, which measures how much air you can exhale and how quickly you can do it. COPD is diagnosed using spirometry, and another test called the diffusion capacity test, which measures how well oxygen moves from your lungs into your bloodstream.
In conclusion, emphysema, and COPD have many symptoms, but there are crucial distinctions that I think will aid diagnosis. Lung illness symptoms should be treated immediately by a doctor.
Treatment Options: Managing Emphysema vs. COPD
Emphysema and COPD have no cure, although numerous treatments may control symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment approaches depend on the severity and other health conditions.
- Medications Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and antibiotics, may treat emphysema and COPD. Bronchodilators relax airway muscles, improving airflow. Antibiotics and corticosteroids may lessen lung inflammation.
- Oxygen Therapy may be necessary for individuals with severe emphysema or COPD who have low oxygen levels in their blood. Supplemental oxygen can improve breathing and increase energy levels. Several types of oxygen therapy include portable oxygen tanks, concentrators, and liquid oxygen systems.
3. Pulmonary Rehabilitation is a program that includes exercise, breathing techniques, and education on managing symptoms of emphysema and COPD.
Pulmonary rehabilitation improves lung function, symptoms, and quality of life.
4. Emphysema and COPD may need surgery in severe situations. Lung volume reduction surgery eliminates diseased lung tissue, improving airflow. End-stage emphysema and COPD patients may need lung transplants.
5. Lifestyle Changes Lifestyle adjustments may reduce COPD and emphysema symptoms. Emphysema and COPD patients should quit Smoking. Avoiding lung irritants like air pollution and chemicals might also assist. Healthy eating and exercise may enhance health and minimize discomfort.
In conclusion, emphysema, and COPD have no cure, although numerous treatments may control symptoms and enhance the quality of life. Work with your doctor to create a treatment plan for emphysema or COPD. Emphysema and COPD patients may live entire, active lives with adequate care.
Prevention: Strategies to Reduce the Risk of Emphysema and COPD
There are various ways to lower the risk of emphysema and COPD, including genetics.
- Quit Smoking. The most important step individuals can take to reduce their risk of emphysema and COPD is to quit Smoking. Smoking is the leading cause of emphysema and COPD, and quitting can significantly reduce the risk of developing these conditions. If you need help to quit Smoking, talk to your healthcare provider or join a smoking cessation program.
- Avoid Exposure to Lung Irritants. Avoiding air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust may help lower the risk of emphysema and COPD. Workers in these sectors should wear masks or use ventilation systems to protect their lungs.
- Exercise Regularly. Regular exercise can help improve lung function and reduce the risk of emphysema and COPD. Exercise can also improve overall health and reduce the risk of other chronic conditions that may increase the risk of emphysema and COPD, such as heart disease and diabetes.
- Maintaining a healthy diet can also reduce the risk of emphysema and COPD.
A diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein may help the body maintain optimum lung function.
- Get Regular Check-Ups. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify early signs of emphysema and COPD. Early detection can improve the chances of successful treatment and management of symptoms.
In conclusion, genetics can’t be altered, but people may minimize their chances of emphysema and COPD by taking preventive measures. Emphysema and COPD may be prevented by quitting Smoking, avoiding lung irritants, exercising, eating well, and having regular checkups. These preventive measures may boost lung health and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
Living with Emphysema and COPD: Coping Strategies and Support
Emphysema and COPD may be difficult to manage, but coping skills and support can help.
- Your Condition, Emphysema and COPD education, may assist patients in comprehending their symptoms and treatments. Healthcare practitioners may explain the disease and propose patient advocacy organizations.
- Follow a Treatment Plan. Following a treatment plan can help individuals manage their symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment plans may include medication, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lifestyle changes.
- Stay Active and Engaged Despite the limitations that emphysema and COPD may impose, individuals need to stay active and engaged. This can help improve physical and mental well-being. Activities may include hobbies, socializing, and exercise.
- Support from friends, family, and healthcare providers can be invaluable in managing the challenges of living with emphysema and COPD. Joining a support group or connecting with others who are also living with the condition can provide additional support and understanding.
- Practicing self-care is essential for managing emphysema and COPD, which may be stressful. This may involve resting, eating well, and relaxing with yoga or meditation.
Managing emphysema and COPD is tough, but coping techniques may enhance the quality of life.
Learning about emphysema and COPD, following a treatment plan, staying active, getting help, and practicing self-care may help people live well. These methods alleviate symptoms and improve health.
Conclusion about Emphysema vs. COPD
Emphysema and COPD can impact an individual’s quality of life. Avoiding harmful environmental exposures can reduce the risk of developing these conditions. Managing symptoms with treatment, staying active, seeking support, and practising self-care can improve overall well-being. By working with healthcare providers and seeking help, individuals can take control of their health and maintain a fulfilling life.
Reference
American Lung Association. (2021). Emphysema. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/emphysema
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). COPD. https://www.cdc.gov/copd/index.html
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2021). What is COPD? https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/copd
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. (2021). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of COPD.
https://goldcopd.org/gold-reports/

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.