January 21, 2026 Last Updated: January 21, 2026
Lips edema is when your lips suddenly become swollen, puffy, or larger than normal. This can happen from allergic reactions, injuries, infections, or underlying health conditions. The good news? Most cases can be treated at home with ice and antihistamines, though severe swelling needs immediate medical attention.
Key Takeaways
✅ Lips edema usually results from allergies, injuries, or infections
✅ Cold compresses and antihistamines treat most mild cases
✅ Seek emergency care for breathing difficulty or rapid swelling
✅ Angioedema requires medical evaluation and specific treatment
✅ Prevention through trigger identification is most effective
✅ Keep emergency supplies available if you have severe reactions
✅ Nutritional deficiencies can contribute to chronic lip problems
✅ Document patterns to identify your personal triggers
My Personal Experience with Lip Swelling
I’ll never forget the morning I woke up and couldn’t recognize my own face in the mirror. My upper lip had ballooned to twice its normal size overnight. I panicked, thinking I’d developed some rare disease.
After rushing to urgent care, I discovered I had an allergic reaction to a new toothpaste I’d started using the night before. The doctor explained that lip edema is quite common and usually harmless when you know what’s causing it.
That scary experience taught me everything I now share with you in this guide. I’ve spent years researching, consulting with allergists, and tracking my own triggers.
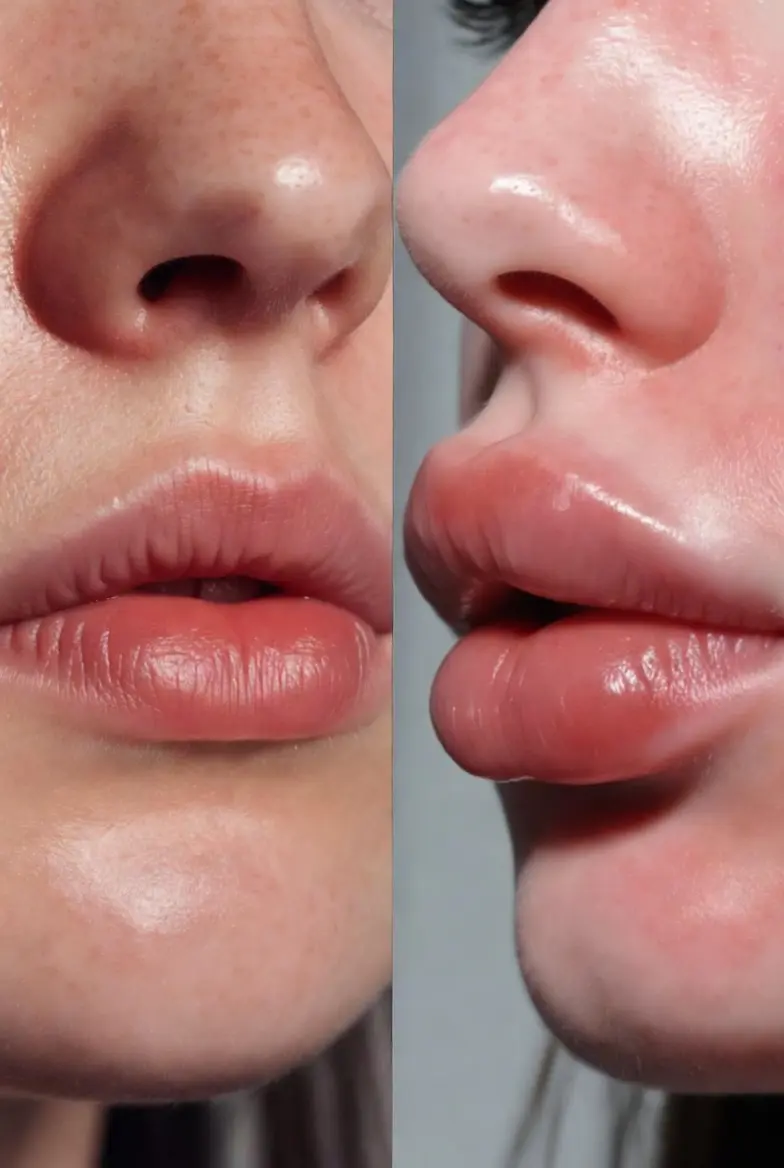
What Exactly is Lips Edema?
Lip edema means fluid buildup in the soft tissue of your lips. Think of it like a sponge soaking up water—except the sponge is your lip tissue.
Your lips can swell for three main reasons:
- Blood vessels leak fluid into the surrounding tissue
- Inflammation triggers your body’s protective response
- Physical trauma damages the delicate lip area
Quick Facts About Lip Swelling
📌 Key Statistics –
- Affects approximately 15-20% of people at least once in their lifetime
- Allergic reactions cause 40% of sudden lip swelling cases
- Most episodes are resolved within 24-48 hours without treatment
Common Causes of Lips Edema
Allergic Reactions (Most Frequent Cause)
I’ve seen countless people struggle with allergic lip swelling without realizing what triggered it. Food allergies top the list.
Common Food Triggers –
- Shellfish and fish
- Peanuts and tree nuts
- Eggs and dairy products
- Strawberries and citrus fruits
- Wheat and soy products
Medication-Related Swelling –
Your medications might be the hidden culprit. I learned this the hard way when my blood pressure medication caused my lips to swell periodically.
| Medication Type | Risk Level | Common Examples |
| ACE Inhibitors | High | Lisinopril, Enalapril |
| NSAIDs | Medium | Ibuprofen, Aspirin |
| Antibiotics | Medium | Penicillin, Amoxicillin |
| Blood Thinners | Low- Medium | Warfarin |
Angioedema Lips – The Deep Swelling
Angioedema goes deeper than surface swelling. It affects layers beneath your skin and can be life-threatening if it spreads to your throat.
Warning Signs of Severe Angioedema –
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Tongue swelling along with the lips
- Sudden drop in blood pressure
- Dizziness or fainting
Important Note – If you experience breathing difficulty with lip swelling, call 911 immediately. This is a medical emergency, not something to “wait out.”
Injuries and Physical Trauma
Lip edema after injury happens more often than you’d think. I once bit my lip while eating and woke up the next morning looking like I’d been in a fight.
Common Injury Causes –
- Accidental lip biting during meals or sleep
- Sports injuries (basketball, boxing, hockey)
- Falls or direct blows to the mouth
- Dental procedures or braces irritation
- Lip piercings or cosmetic injections
Infections That Cause Lip Inflammation
Bacterial and viral infections love the warm, moist environment around your lips.
Infection Types –
Cold Sores (Herpes Simplex) –
- Start with tingling before swelling appears
- Develop into fluid-filled blisters
- Contagious through direct contact
- Recur when the immune system is weak
Bacterial Infections –
- Cellulitis (deeper skin infection)
- Impetigo (crusty, golden-colored sores)
- Angular cheilitis (cracked, infected corners)
Weather and Environmental Factors
Suddenly, swollen lips from sun exposure surprised me during my first beach vacation. I hadn’t realized lips need sunscreen, too!
Environmental Triggers –
- Severe sunburn on the lips
- Extreme cold is causing chapping and swelling
- Wind exposure leading to dryness
- Low-humidity environments
- Air pollution and smoke
Fewer Common Medical Causes
Hereditary Angioedema
This genetic condition runs in families and causes unpredictable swelling episodes. My cousin has this, and she carries emergency medication everywhere.
Key Characteristics –
- Begins in childhood or teenage years
- No hives or itching (unlike allergies)
- Affects hands, feet, face, and intestines
- Episodes last 2-5 days typically
- Triggered by stress, injury, or hormones
Autoimmune Conditions
What autoimmune disease causes lip swelling? Several conditions can trigger this response:
- Lupus – Causes facial swelling and butterfly rash
- Crohn’s Disease – Creates granulomatous inflammation
- Sarcoidosis – Forms inflammatory nodules
- Melkersson-Rosenthal Syndrome – A rare condition causing recurrent lip swelling
Nutritional Deficiencies
What vitamin deficiency causes swollen lips? I discovered this connection through my health journey.
Deficiencies Linked to Lip Problems:
| Nutrient | Role | Deficiency Signs |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | Skin health | Cracked, swollen lips; corner sores |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | Inflammation control | Swollen, red tongue and lips |
| Vitamin B12 | Nerve and blood health | Pale, swollen, burning lips |
| Iron | Oxygen transport | Pale, smooth, swollen lips |
| Zinc | Immune function | Slow healing, recurring swelling |
Recognizing Swollen Lips Symptoms
Understanding swollen lips symptoms helps you know when to worry and when to relax.
Mild Symptoms (Home Treatment OK)
✓ Slight puffiness on one or both lips
✓ No breathing difficulty
✓ Redness without severe pain
✓ Can eat and drink normally
✓ Known trigger (like spicy food)
Moderate Symptoms (Monitor Closely)
⚠️ Noticeable swelling affecting lip shape
⚠️ Mild difficulty eating or speaking
⚠️ Tingling or numbness sensations
⚠️ Swelling lasting more than 24 hours
⚠️ Recurring episodes without an obvious cause
Severe Symptoms (Seek Emergency Care)
When to Worry About Lip Swelling:
- Rapid swelling within minutes
- Breathing becomes difficult
- Throat feels tight or closing
- Tongue swells simultaneously
- Severe pain or burning
- Signs of infection (fever, pus, red streaks)
- Loss of consciousness or confusion
Effective Lip Inflammation Treatment
Immediate First Aid Steps
When my lips swell now, I follow this exact protocol I developed with my allergist.
Step-by-step response –
- Stop the Trigger – Remove food, medication, or product immediately
- Apply Cold Compress – Wrap ice in a clean cloth, apply 10 minutes on, 10 minutes off
- Take an antihistamine – Benadryl or Zyrtec for allergic swelling
- Elevate Your Head – Prop yourself up to reduce fluid accumulation
- Stay Hydrated – Drink water to help flush allergens
Swollen Lips Home Remedies
I’ve tested dozens of natural remedies. These actually work:
Proven Natural Treatments –
Aloe Vera Gel –
- Reduces inflammation quickly
- Soothes burning sensations
- Apply directly from the plant or pure gel
- Use 3-4 times daily
Honey Application –
- Natural antibacterial properties
- Moisturizes while healing
- Leave on for 15-20 minutes
- Works best for minor swelling
Turmeric Paste –
- Mix turmeric powder with water
- Anti-inflammatory compound curcumin
- Apply a thin layer to the affected area
- May stain temporarily (heads up!)
Chamomile Tea Compress –
- Brew strong chamomile tea
- Cool completely in the refrigerator
- Soak a clean cloth and apply
- Repeat every few hours
Over-the-counter medications
For Allergic Reactions –
- Antihistamines (Cetirizine, Loratadine)
- Hydrocortisone cream for external use
- Pain relievers if needed (Acetaminophen)
For Infections –
- Antibacterial ointments
- Antiviral creams for cold sores
- Antifungal treatments for angular cheilitis
Related: Eczema Lips: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Tips
When Prescription Treatment is Needed
Some situations require medical intervention. I needed prescription steroids when my angioedema lips didn’t respond to home treatment.
Prescription Options –
- Oral corticosteroids for severe inflammation
- Epinephrine auto-injector for emergencies
- Specific angioedema medications (Icatibant, C1-inhibitor)
- Antibiotic or antiviral prescriptions
Prevention Strategies That Actually Work
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
I keep a “lip swelling diary” on my phone. Sounds silly, but it helped me identify three hidden triggers I’d never have found otherwise.
Tracking Method –
- Note what you ate 2-24 hours before swelling
- Record new products (cosmetics, toothpaste, lip balm)
- Track environmental factors (weather, location)
- Document stress levels and activities
- Pattern recognition takes 3-4 episodes, usually
Daily Prevention Habits
Morning Routine –
- Apply SPF 30+ lip balm before sun exposure
- Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products
- Stay hydrated (at least 8 glasses of water daily)
- Take daily vitamins if deficient
Evening Routine –
- Remove all lip products before bed
- Apply healing lip treatment
- Use a humidifier in dry climates
- Avoid late-night allergenic foods
Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary Adjustments –
I switched to an anti-inflammatory diet and noticed 70% fewer swelling episodes.
Foods to Increase –
- Omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, walnuts)
- Berries are rich in antioxidants
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Turmeric and ginger
- Green tea
Foods to Limit –
- Processed foods with additives
- High-sodium items
- Artificial sweeteners
- Alcohol (dehydrating)
- Known personal triggers
Special Situations and Considerations
Lip Swelling During Pregnancy
Pregnancy hormones can cause facial angioedema even without a prior history.
Safe Treatments During Pregnancy –
- Cold compresses (completely safe)
- Elevation and rest
- Approved antihistamines (consult OB-GYN first)
- Avoid most medications unless prescribed
Children and Lip Edema
Kids experience swollen lips differently from adults. My nephew taught me this when his peanut allergy first appeared.
Pediatric Considerations –
- Food allergies often emerge in early childhood
- Kids may not articulate symptoms clearly
- Watch for excessive drooling
- Monitor eating and drinking ability
- Keep the Benadryl dosage chart handy
Elderly Patient Concerns
Medication interactions cause more lip swelling in older adults.
Age-Related Factors –
- Multiple medications increase risk
- Thinner, more fragile skin
- Slower healing processes
- Higher risk of complications
- Need careful medication review
When Medical Evaluation is Essential
Red Flags Requiring a Doctor Visit
Schedule Appointment If –
- Swelling lasts more than 48 hours
- Recurring episodes (more than 3 times monthly)
- No identifiable trigger
- Affecting quality of life
- Accompanied by other symptoms (rashes, joint pain)
Diagnostic Tests Your Doctor Might Order
Common Testing –
- Allergy skin tests or blood tests
- C1-inhibitor level testing
- Complete blood count
- Vitamin and mineral panels
- Autoimmune markers
- Thyroid function tests
Living with Chronic Lip Swelling
Emergency Preparedness
I carry an emergency kit everywhere now. Here’s what’s inside:
Essential Emergency Kit –
- Epinephrine auto-injector (if prescribed)
- Fast-acting antihistamines
- Medical alert card with triggers
- Emergency contact information
- List of current medications
- A cold pack that activates by squeezing
Building Your Support Network
Tell These People About Your Condition –
- Family members and close friends
- Workplace supervisor or HR
- School nurses (for children)
- Dining companions
- Travel partners
Frequently Asked Questions About Lips Edema
What causes edema in the lips?
Lip edema develops when fluid accumulates in lip tissue because of allergic reactions (food, medication, environmental), physical injuries, infections like cold sores or cellulitis, angioedema (deep tissue swelling), autoimmune diseases, or nutritional deficiencies. The most common cause is allergic reactions to food or medications.
How to get rid of lip angioedema?
Angioedema lips require immediate cold compress application, antihistamines for mild cases, and prescription medications for severe episodes. Contact your doctor for persistent angioedema.
Emergency treatment may include epinephrine injections, corticosteroids, or specialized angioedema medications like C1-inhibitor concentrates. Never attempt to treat severe angioedema at home.
What is the best cure for swollen lips?
The best lip inflammation treatment depends on the cause. For allergies, take antihistamines and apply ice. For injuries, use cold compresses and elevation. For infections, apply appropriate antibacterial or antiviral treatments.
Most importantly, identify and remove the trigger. Severe cases need medical evaluation and prescription medications.
What autoimmune disease causes lip swelling?
Several autoimmune conditions cause lip swelling: Crohn’s disease (granulomatous cheilitis), lupus (facial edema), sarcoidosis (granuloma formation), Skijoring’s syndrome (dry, swollen lips), and Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome (recurrent facial swelling).
Lupus and Crohn’s disease are most associated with chronic lip inflammation.
What vitamin deficiency causes swollen lips?
Vitamin B deficiencies primarily cause lip swelling. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) deficiency creates cracked, swollen lips and angular cheilitis. Vitamin B3 (niacin) deficiency causes red, inflamed lips and tongue. Vitamin B12 deficiency results in pale, burning, swollen lips. Iron and zinc deficiencies also contribute to chronic lip inflammation and poor healing.
Conclusion
Lips edema doesn’t have to control your life. Through my journey from panicked patient to informed advocate, I’ve learned that knowledge truly is power.
Most episodes resolve quickly with simple home treatments. The key is recognizing your triggers, responding appropriately, and knowing when to seek medical help.
Start keeping track of your episodes today. Note what you ate, what products you used, and environmental factors. Patterns will emerge, and you’ll gain control.
Remember—you’re not alone in this. Millions experience lip swelling regularly. With the strategies in this guide, you’re now equipped to handle whatever causes your lips to swell.
Stay safe, stay informed, and don’t hesitate to seek medical attention when something feels wrong. Your health is worth it.
References
Cleveland Clinic – “Angioedema: Causes, Symptoms, Types & Treatments”
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22632-angioedema
Medical News Today – “Swollen Lips: Causes and Treatment”
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321080
Disclaimer: I am not a medical doctor, and this content does not replace professional medical advice. What I share comes from real-life experience, extensive research, and consultation with healthcare providers. Always consult qualified medical professionals for diagnosis and treatment of any health condition.

Adel Galal is a health and wellness writer with over 30 years of experience studying and writing about health, fitness, nutrition, and healthy living. He is the founder of NextFitLife.com, where he shares practical, evidence-based guidance to support long-term health at any age. Adel’s mission is simple:
to help people make smarter health choices that fit real life, at any age.



